Designing an Off-Grid Solar Panel System for Sustainable Energy Solutions
Off-Grid Solar Panel Systems A Sustainable Solution for Energy Independence
As the global demand for renewable energy continues to rise, off-grid solar panel systems have emerged as an effective solution for individuals and communities seeking energy independence. These systems harness solar energy to power homes and businesses without relying on traditional electrical grids. This article delves into the key components, benefits, challenges, and applications of off-grid solar panel systems.
What is an Off-Grid Solar Panel System?
An off-grid solar panel system consists of solar panels, a charge controller, batteries, and an inverter. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, while the charge controller regulates the flow of energy to the batteries, preventing overcharging. The batteries store energy for use when sunlight is not available, such as during the night or cloudy days. Finally, the inverter transforms the direct current (DC) electricity stored in the batteries into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is compatible with household appliances.
Benefits of Off-Grid Solar Systems
1. Energy Independence One of the most significant advantages of off-grid solar systems is the independence they provide from utility companies. Homeowners can produce their energy, reducing their reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating the impact of fluctuating energy prices.
2. Environmental Impact Solar energy is a renewable resource, and off-grid systems significantly decrease greenhouse gas emissions. By utilizing solar power, individuals can contribute to the fight against climate change and promote a cleaner environment.
3. Cost Savings Although the initial investment in an off-grid solar system can be substantial, long-term savings on electricity bills make it a cost-effective choice. In many cases, government incentives and rebates can further reduce the upfront costs.
4. Scalability and Flexibility Off-grid systems can be tailored to specific energy needs, making them suitable for various applications. Whether it's a small cabin in the woods or a larger home, these systems can be customized and expanded as necessary.
5. Remote Access For those living in rural or remote areas where access to the electrical grid is limited or non-existent, off-grid solar systems provide a reliable source of energy, enabling modern conveniences and enhancing quality of life.
solar panel off grid system
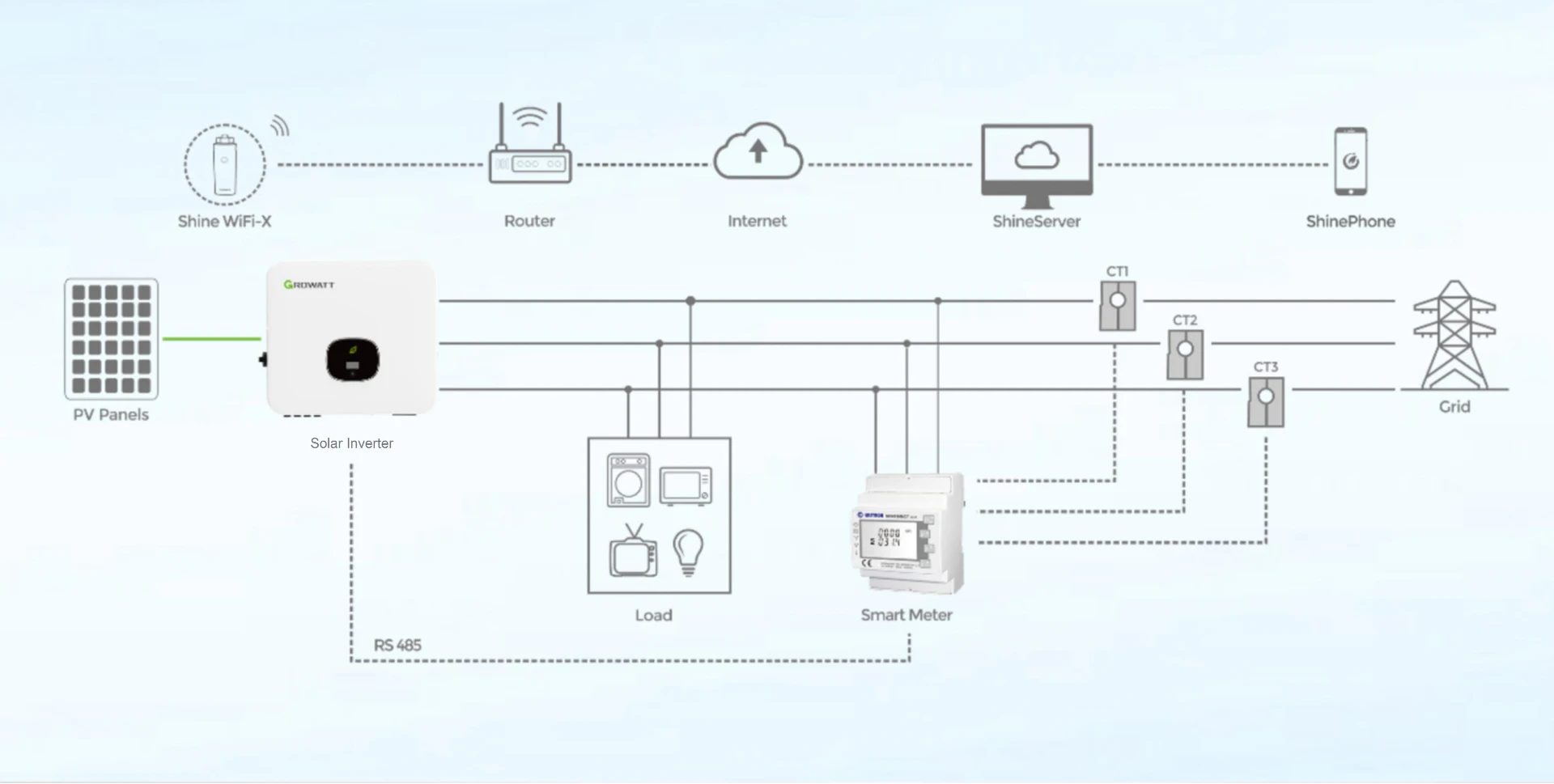
Challenges of Off-Grid Solar Systems
Despite their numerous advantages, off-grid solar panel systems come with challenges.
1. Initial Cost The upfront costs of purchasing and installing an off-grid solar system can be high. This initial investment can be a barrier for some individuals, even though costs have been steadily decreasing over the years.
2. Energy Storage Limitations Batteries play a crucial role in off-grid systems, but they have limitations in terms of capacity and lifespan. Users must carefully assess their energy consumption and battery storage needs to ensure a reliable supply of electricity.
3. Weather Dependence Solar energy generation is dependent on sunlight, making it less reliable in regions with frequent cloud cover or low sunlight. Users may need to have backup generators or alternative power sources to supplement their energy needs during extended periods of inclement weather.
4. Technical Knowledge While technology has made off-grid systems more user-friendly, some level of technical knowledge is still required for installation and maintenance. Users should be prepared to invest time in learning how to operate and troubleshoot their systems effectively.
Applications of Off-Grid Solar Systems
Off-grid solar panel systems are becoming increasingly popular in a variety of settings. They are commonly used in rural homes, outdoor cabins, and recreational vehicles (RVs). Additionally, off-grid systems are being deployed in developing countries to provide electricity to communities without access to traditional power sources. Solar installations on farms can power irrigation systems or equip rural schools with electricity, facilitating education and improving livelihoods.
Conclusion
Off-grid solar panel systems present a compelling solution for those seeking energy independence and sustainability. With the combined benefits of environmental stewardship and cost savings, these systems offer an innovative approach to tackling modern energy challenges. Although there are challenges to be navigated, the potential for a more sustainable and independent energy future makes off-grid solar systems a viable option for many. As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, we can expect to see a growing implementation of these systems worldwide, paving the way for a greener, more self-sufficient future.
-
Unlocking Energy Freedom with the Off Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Unlock More Solar Power with a High-Efficiency Bifacial Solar PanelNewsJun.06,2025
-
Power Your Future with High-Efficiency Monocrystalline Solar PanelsNewsJun.06,2025
-
Next-Gen Solar Power Starts with Micro Solar InvertersNewsJun.06,2025
-
Harnessing Peak Efficiency with the On Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Discover Unmatched Efficiency with the Latest String Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025







