Comparison of Bifacial and Monofacial Solar Panels Performance and Efficiency
Bifacial vs. Monofacial Solar Panels A Comparative Analysis
In the rapidly evolving field of solar energy, bifacial and monofacial solar panels have garnered significant attention from researchers, manufacturers, and consumers alike. Both types of panels play crucial roles in harnessing solar energy, but they have distinct features, advantages, and applications that can impact their efficiency and effectiveness.
Bifacial vs
. Monofacial Solar Panels A Comparative AnalysisOn the other hand, bifacial solar panels are designed to capture sunlight on both sides, enabling them to harness reflected sunlight from surfaces like rooftops or the ground. This unique design can significantly enhance their overall energy production. Bifacial panels are particularly advantageous in installations with high albedo surfaces, such as snowy landscapes or white roofs, where reflected sunlight can boost energy output.
panel bifacial vs monofacial
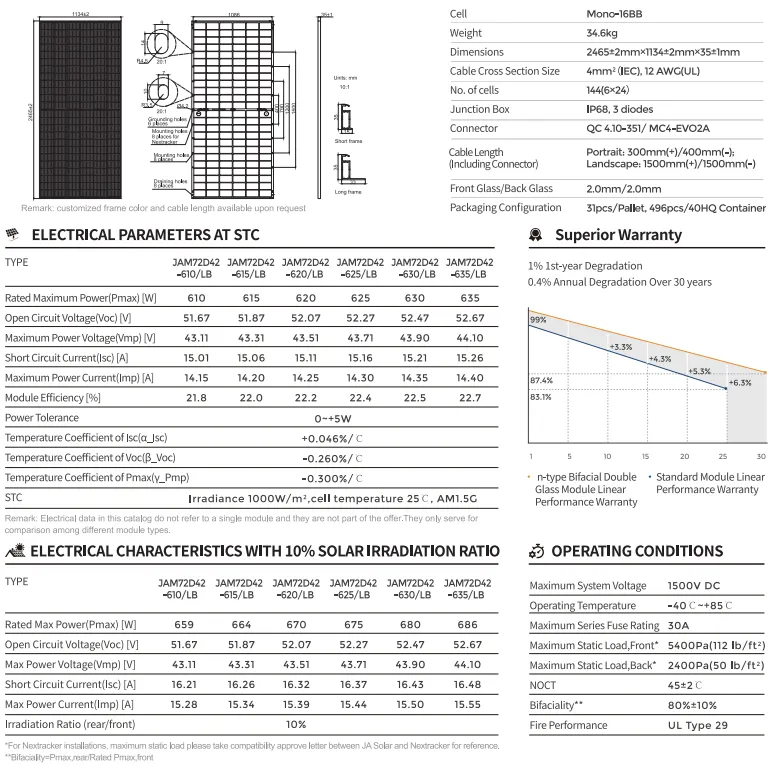
One of the key advantages of bifacial solar technology is its higher efficiency. Studies have shown that bifacial panels can yield 10-20% more energy than their monofacial counterparts under optimal conditions. This makes them an appealing choice for large-scale solar farms and utility-scale projects where maximizing energy output is crucial for profitability.
Cost considerations, however, play a significant role in the choice between bifacial and monofacial panels. While bifacial panels may offer superior efficiency, they tend to have a higher initial investment cost. This can deter some users, particularly in residential applications where budget constraints are a primary concern. Yet, the long-term savings from increased energy production can often justify the upfront costs, especially in regions with ample sunlight.
Installation and maintenance also differ between the two types of panels. Bifacial panels require specific mounting structures to maximize their energy absorption from both sides. This might entail additional planning and investment during the installation process. However, once installed, both types of panels generally require similar maintenance, making them relatively easy to manage.
In conclusion, the choice between bifacial and monofacial solar panels ultimately depends on the specific needs of the user and the characteristics of the installation site. For large projects aiming for maximum efficiency and output, bifacial panels may offer more significant advantages. Conversely, for residential installations where cost is a primary factor, monofacial panels remain a solid choice. As solar technology continues to advance, understanding these differences is vital for making informed decisions in the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions.
-
Unlocking Energy Freedom with the Off Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Unlock More Solar Power with a High-Efficiency Bifacial Solar PanelNewsJun.06,2025
-
Power Your Future with High-Efficiency Monocrystalline Solar PanelsNewsJun.06,2025
-
Next-Gen Solar Power Starts with Micro Solar InvertersNewsJun.06,2025
-
Harnessing Peak Efficiency with the On Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Discover Unmatched Efficiency with the Latest String Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025







