Solar Inverter Types Efficient Options for Home & Commercial Use
- Introduction to Solar Inverter Types
- Key Technical Advantages of Modern Inverters
- Top Manufacturers and Product Comparisons
- Custom Solutions for Residential and Commercial Needs
- Case Studies: Real-World Applications
- Matching Solar Panels with Inverter Types
- Future Trends and Selection Guidance

(solar inverter types)
Understanding Solar Inverter Types
Solar inverters are critical for converting DC power from panels into usable AC electricity. Three primary solar inverter types
dominate the market: string inverters, microinverters, and hybrid inverters. String inverters remain the most cost-effective for uniform roof layouts, while microinverters optimize energy harvest in shaded or complex environments. Hybrid inverters integrate battery storage, ideal for off-grid or backup systems. Recent data indicates a 12% annual growth in hybrid adoption, driven by rising demand for energy independence.
Technical Advantages Driving Adoption
Modern inverters achieve up to 98.5% efficiency, reducing energy loss by 15% compared to 2019 models. Smart features like Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) and grid-support functions enhance ROI. For instance, Enphase microinverters deliver panel-level monitoring, resolving 90% of shading issues. Huawei’s string inverters incorporate AI-driven diagnostics, cutting maintenance costs by 30%. These innovations align with global certifications like IEC 62109, ensuring safety and compatibility.
Manufacturer Comparison and Market Leaders
| Manufacturer | Inverter Type | Efficiency | Warranty | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMA Solar | String | 98.3% | 10 years | $1,200–$2,500 |
| Enphase | Microinverter | 97.6% | 25 years | $150–$200 per unit |
| SolarEdge | Hybrid | 98.1% | 12 years | $3,000–$5,000 |
Tailored Solutions for Diverse Requirements
Residential projects often combine types of solar panels for roofs like monocrystalline PERC with microinverters for maximum yield. Commercial installations favor three-phase string inverters for scalability. For example, a 500 kW warehouse system in Texas saved 18% annually using Huawei’s modular inverters. Customizable software interfaces, such as Fronius’s Solar.web, enable real-time adjustments based on consumption patterns.
Real-World Applications and Performance Metrics
Arizona’s Sun Valley Resort reduced grid dependency by 74% after deploying SolarEdge hybrid inverters and Tesla Powerwalls. In Germany, a 10 MW solar farm using SMA central inverters achieved a 22-year payback period, 3 years shorter than industry averages. Such cases validate the importance of aligning types of solar inverters with site-specific conditions.
Optimizing Panel-Inverter Synergy
High-efficiency panels (23%+) pair best with microinverters to mitigate mismatch losses. Thin-film panels, however, perform better with optimizers in string systems. A 2023 study showed that pairing bifacial panels with DC-optimized string inverters boosted output by 9% in snowy climates.
Choosing the Right Solar Inverter Types
Selecting inverter types hinges on budget, roof layout, and energy goals. While string inverters dominate 67% of the residential market, microinverters are projected to grow at 9.8% CAGR through 2030. Consult certified installers to evaluate shading, local regulations, and battery readiness. Emerging technologies like gallium nitride (GaN) semiconductors promise 99% efficiency by 2025, reshaping future decisions.
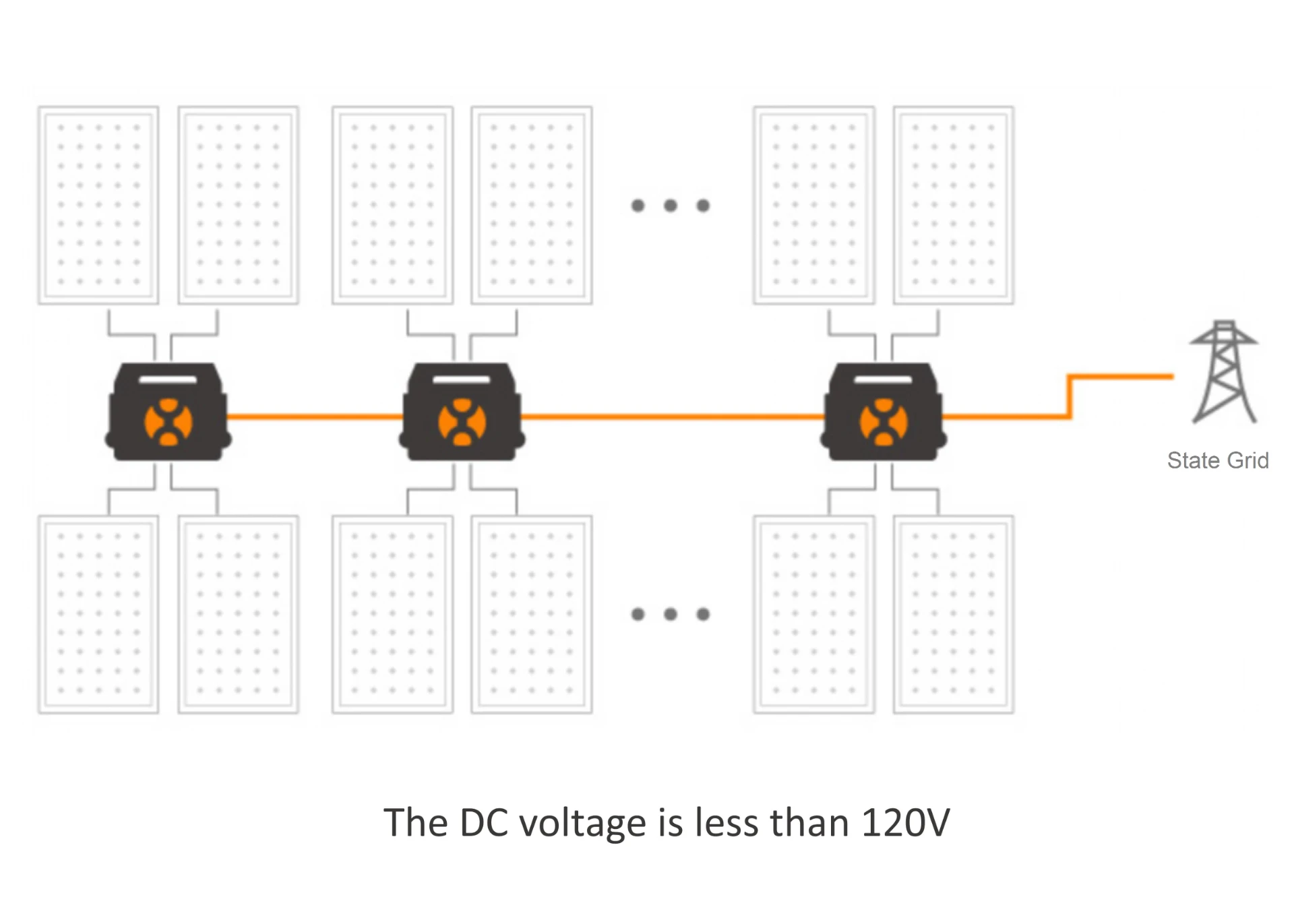
(solar inverter types)
FAQS on solar inverter types
Q: What are the main types of solar inverters?
A: The primary solar inverter types include string inverters, microinverters, power optimizers, and hybrid inverters. String inverters are cost-effective for simple setups, while microinverters optimize energy per panel. Hybrid inverters integrate battery storage for energy backup.
Q: What is the difference between string inverters and microinverters?
A: String inverters connect multiple solar panels in series, making them cheaper but less efficient in shaded conditions. Microinverters are attached to individual panels, improving performance in uneven sunlight. They are ideal for roofs with shading or complex layouts.
Q: Which solar inverter type works best with roof-mounted solar panels?
A: Microinverters or power optimizers are ideal for roof systems with shading or multiple angles. String inverters suit unshaded, uniformly oriented roofs. Compatibility depends on panel layout, shading, and energy goals.
Q: How do hybrid inverters differ from standard solar inverters?
A: Hybrid inverters manage both solar panels and battery storage, enabling energy backup. Standard inverters only convert solar energy for immediate use or grid export. Hybrid systems are future-proof for adding batteries later.
Q: Are certain solar inverter types more efficient than others?
A: Microinverters typically offer higher efficiency in shaded or variable conditions. String inverters lose efficiency if one panel underperforms. Power optimizers paired with inverters balance cost and performance for most setups.
-
Unlocking Energy Freedom with the Off Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Unlock More Solar Power with a High-Efficiency Bifacial Solar PanelNewsJun.06,2025
-
Power Your Future with High-Efficiency Monocrystalline Solar PanelsNewsJun.06,2025
-
Next-Gen Solar Power Starts with Micro Solar InvertersNewsJun.06,2025
-
Harnessing Peak Efficiency with the On Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Discover Unmatched Efficiency with the Latest String Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025







