average cost to install solar panels
Average Cost to Install Solar Panels
As the demand for sustainable energy sources continues to rise, many homeowners and businesses are considering solar power as a viable alternative. Installing solar panels not only contributes to reducing carbon emissions but also provides significant long-term savings on energy bills. However, one of the main concerns for those contemplating this switch is the average cost to install solar panels.
The total cost of installing solar panels can vary widely depending on several factors, including the size of the system, the type of technology used, geographical location, and installation complexities. On average, the cost of solar panel installation in the United States ranges from $15,000 to $25,000 for a residential system that can typically generate between 5-10 kW of power. This translates to approximately $2.50 to $3.50 per watt, which is a common metric used in the solar industry.
One of the most significant influences on the total cost is the size of the solar panel system. Larger systems with higher energy production potential will obviously incur higher overall costs, but they may also provide more substantial savings on energy bills and increased property value. Homeowners are encouraged to assess their electricity consumption to determine the ideal system size for their needs.
average cost to install solar panels
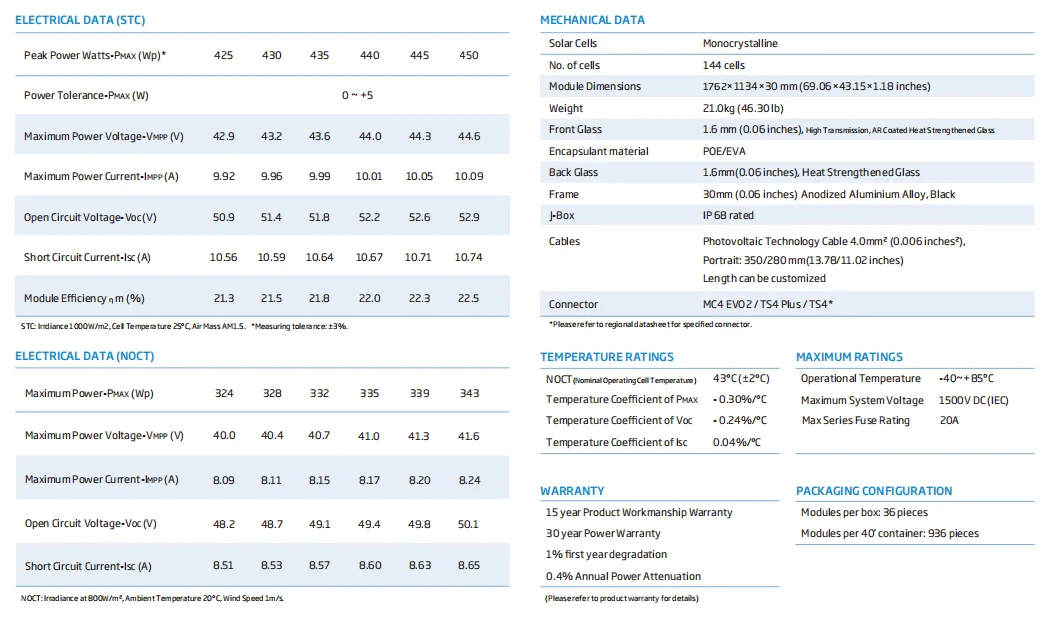
Another important factor is the type of solar panels chosen for installation. There are primarily three types of solar panels monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film. Monocrystalline panels tend to be the most efficient and have the highest price point, although they take up less space on a roof. Polycrystalline panels are generally less expensive but offer slightly lower efficiency. Thin-film panels are less common but are lighter and more flexible, suitable for specific applications. Each option presents different cost implications that homeowners should consider.
Geographical location plays a crucial role in installation costs as well. States with higher sunlight exposure can expect more savings due to increased energy production, which in turn can offset installation costs quicker. Additionally, local incentives, rebates, and tax credits can significantly reduce the upfront costs. For instance, the federal solar tax credit allows homeowners to deduct a percentage of the installation costs from their federal taxes.
Installation labor costs can also vary depending on regional pricing, with urban areas typically incurring higher labor fees compared to rural locations. Moreover, the complexity of the installation process, such as roof type and structural considerations, can further influence costs.
In conclusion, the average cost to install solar panels can range significantly based on system size, technology, location, and installation complexity. While the upfront investment may seem daunting, various incentives and the potential for significant savings on energy bills make solar energy an increasingly attractive option for homeowners. As technology continues to improve and prices decrease, solar panels are likely to become an even more accessible and appealing choice for clean energy.
-
Unlocking Energy Freedom with the Off Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Unlock More Solar Power with a High-Efficiency Bifacial Solar PanelNewsJun.06,2025
-
Power Your Future with High-Efficiency Monocrystalline Solar PanelsNewsJun.06,2025
-
Next-Gen Solar Power Starts with Micro Solar InvertersNewsJun.06,2025
-
Harnessing Peak Efficiency with the On Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Discover Unmatched Efficiency with the Latest String Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025







