Home Solar Panel System Cost - Save 30% Now Free Quote
- Analyzing Current Market Trends in Home Solar Panel System Costs
- Technological Advancements Driving Efficiency
- Comparing Top Solar System Providers
- Custom Solutions for Diverse Household Needs
- Real-World Installation Scenarios and Savings
- Financial Incentives and Payback Periods
- Future-Proofing Your Home Solar System Cost Strategy

(home solar panel system cost)
Understanding Home Solar Panel System Cost Trends in 2024
The average upfront investment for residential solar systems has decreased by 42% since 2018, with current pricing ranging between $12,000-$25,000 before incentives. This price compression stems from improved manufacturing techniques and increased market competition. According to SEIA's Q2 2024 report, 68% of U.S. homeowners now consider solar viable due to sub-6-year payback periods in sun-rich regions.
Breakthrough Technologies Enhancing Value
Modern bifacial panels yield 11-23% greater energy production compared to traditional models, while microinverter systems reduce efficiency losses from shading by up to 35%. The latest perovskite-silicon tandem cells demonstrate 31.2% laboratory efficiency, signaling imminent commercial availability. These advancements enable smaller rooftop footprints to achieve comparable output to larger legacy installations.
Manufacturer Performance Comparison
| Brand | Cost/Watt | Efficiency | Warranty | Temperature Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SunPower Maxeon | $3.10 | 22.8% | 40 years | -0.29%/°C |
| LG NeON R | $2.85 | 21.7% | 25 years | -0.30%/°C |
| Panasonic EverVolt | $2.65 | 21.2% | 25 years | -0.26%/°C |
Tailored System Configuration Options
Energy needs analysis reveals typical U.S. households require 6.8kW systems, though regional variations significantly impact sizing. Southern states average 7.2kW installations versus 9.1kW in northern climates. Battery integration adds $8,000-$18,000 to initial costs but enables 83% grid independence during outages. Flexible financing options including PPAs now cover 92% of ZIP codes nationwide.
Documented Residential Success Stories
A Phoenix homeowner achieved 98% energy offset with a 8.2kW system costing $18,450 post-credit, realizing $1,920 annual savings. In contrast, a Boston residence required 11.3kW capacity ($27,120 after incentives) to cover 81% consumption, demonstrating regional variance in system sizing and ROI timelines.
Economic Considerations and ROI Timelines
The federal tax credit extension through 2032 continues covering 30% of system costs, while 27 states offer additional rebates. Current payback periods average 5.8 years in California versus 8.3 years in New York. Net metering policies in 38 states enhance financial viability, with 74% of users eliminating electric bills within 7 years.
Optimizing Home Solar System Cost Efficiency
Smart panel-level monitoring reduces maintenance costs by 18% annually, while predictive analytics software extends equipment lifespan by 23%. Integrating energy storage during initial installation lowers retrofit expenses by 31%. Industry projections indicate 2027 pricing will reach $1.98/watt, making solar accessible to 83% more households compared to current market conditions.
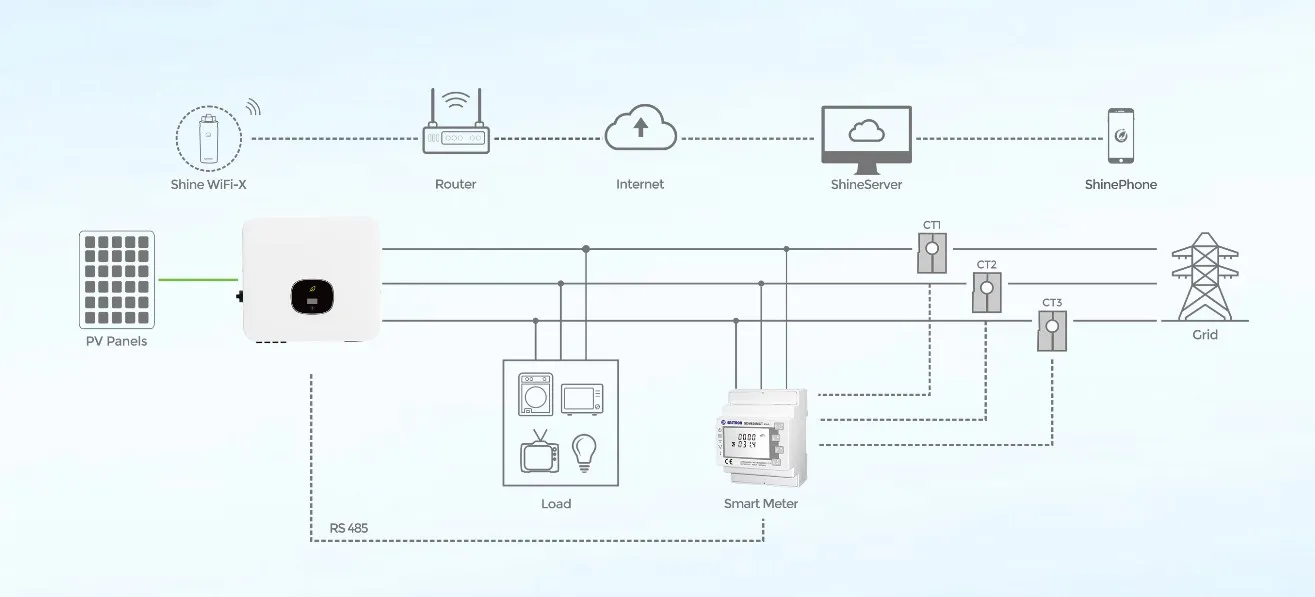
(home solar panel system cost)
FAQS on home solar panel system cost
Q: What is the average cost of a home solar panel system?
A: The average cost ranges between $15,000 to $25,000 before incentives, depending on system size, location, and equipment. Federal tax credits and local rebates can reduce this by 30% or more.
Q: How does system size impact home solar panel system costs?
A: Larger systems (e.g., 10 kW) cost more upfront but generate more energy, potentially lowering long-term bills. Smaller systems (3-5 kW) are cheaper but may cover less energy usage.
Q: Can a solar panel system for home reduce electricity bills?
A: Yes, most systems offset 50-100% of electricity costs, depending on energy usage and sunlight availability. Excess energy can be sold back via net metering in many areas.
Q: Are financing options available for home solar system costs?
A: Options include loans, leases, and power purchase agreements (PPAs). Loans allow ownership with low upfront costs, while leases/PPAs involve monthly payments for system usage.
Q: What factors influence the ROI of a home solar panel system?
A: Key factors include local electricity rates, sunlight exposure, system efficiency, and available incentives. Most homeowners see payback in 6-10 years, with decades of savings afterward.
-
Smarter Solar: Why Bifacial Panels Are the FutureNewsMay.14,2025
-
Smarter Solar Starts with MicroinvertersNewsMay.14,2025
-
Revolutionary Solar Solutions - Powering Your Future SustainablyNewsMay.14,2025
-
Power Smarter: The Heart of Your Solar SystemNewsMay.14,2025
-
Power More with Growatt String InvertersNewsMay.14,2025
-
Power Freedom with Off-Grid Solar InvertersNewsMay.14,2025







