Feb . 13, 2025 21:37
Back to list
the cost of installing solar panels
Exploring the financial implications and overall benefits of installing solar panels is crucial for homeowners and businesses considering this renewable energy option. Solar panel installation costs can differ widely based on several key factors, making each project unique.
Particularly for businesses, the scale of the installation will affect costs. Large-scale commercial installations, while more complex and costly, often benefit from economies of scale, reducing the per-watt cost. Businesses should carefully assess their energy consumption patterns to design a system tailored to their specific needs and maximize efficiency, potentially including battery storage solutions that allow for energy use optimization during peak demands. Financing options present another crucial component. While purchasing the system outright is often the most cost-effective long-term strategy, not every homeowner or business has the capital available. Leasing options, solar loans, and power purchase agreements (PPAs) offer alternative means to manage initial financial outlays, each with distinct advantages and limitations. Financial advisors well-versed in renewable energy investments can provide personalized strategies that align with individual financial situations, further enhancing the sustainability of the investment. Finally, technological advancements continue to reshape the landscape of solar energy. Innovations such as bifacial panels, which capture sunlight on both sides, and improved inverter technologies, increase efficiency and output, making the initial investment more attractive despite slightly higher costs. Keeping abreast of emerging technologies and consulting with industry experts ensures that the chosen system will remain viable and efficient for years to come. Investing in solar panels involves a confluence of factors that extend beyond mere installation costs. By understanding these variables—panel type, installer reputation, geographical incentives, and innovative technologies—consumers can make informed decisions, securing both financial savings and environmental benefits in the transition to renewable energy. Trusting expert insights and leveraging available financial tools makes solar power accessible and practical for a diverse range of energy needs.
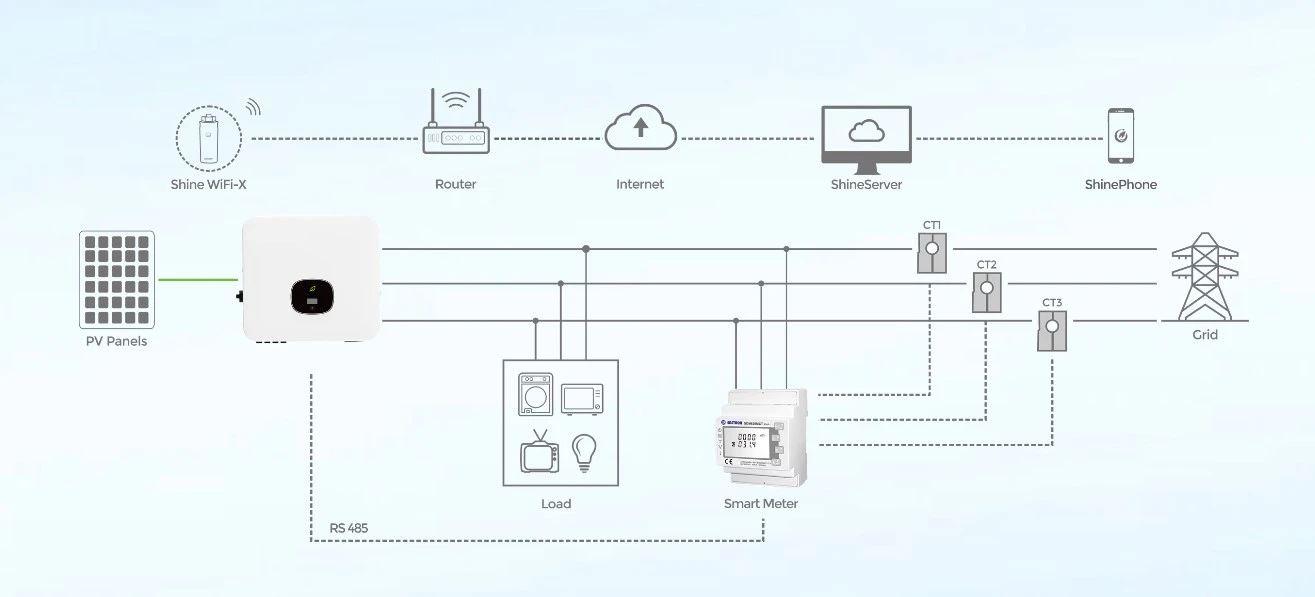

Particularly for businesses, the scale of the installation will affect costs. Large-scale commercial installations, while more complex and costly, often benefit from economies of scale, reducing the per-watt cost. Businesses should carefully assess their energy consumption patterns to design a system tailored to their specific needs and maximize efficiency, potentially including battery storage solutions that allow for energy use optimization during peak demands. Financing options present another crucial component. While purchasing the system outright is often the most cost-effective long-term strategy, not every homeowner or business has the capital available. Leasing options, solar loans, and power purchase agreements (PPAs) offer alternative means to manage initial financial outlays, each with distinct advantages and limitations. Financial advisors well-versed in renewable energy investments can provide personalized strategies that align with individual financial situations, further enhancing the sustainability of the investment. Finally, technological advancements continue to reshape the landscape of solar energy. Innovations such as bifacial panels, which capture sunlight on both sides, and improved inverter technologies, increase efficiency and output, making the initial investment more attractive despite slightly higher costs. Keeping abreast of emerging technologies and consulting with industry experts ensures that the chosen system will remain viable and efficient for years to come. Investing in solar panels involves a confluence of factors that extend beyond mere installation costs. By understanding these variables—panel type, installer reputation, geographical incentives, and innovative technologies—consumers can make informed decisions, securing both financial savings and environmental benefits in the transition to renewable energy. Trusting expert insights and leveraging available financial tools makes solar power accessible and practical for a diverse range of energy needs.
Prev:
Latest news
-
String Solar Inverter: The High-Efficiency Solution for Smart Solar EnergyNewsJul.14,2025
-
Revolutionizing Rooftop Energy with the Power of the Micro Solar InverterNewsJul.14,2025
-
Power Independence with Smart Off Grid Solar Inverter SolutionsNewsJul.14,2025
-
On Grid Solar Inverter: Powering the Future with Smart Grid IntegrationNewsJul.14,2025
-
Monocrystalline Solar Panels: High-Efficiency Power for the Future of Clean EnergyNewsJul.14,2025
-
Bifacial Solar Panel: A Smarter Investment for Next-Generation Energy SystemsNewsJul.14,2025
Related PRODUCTS







