standard dimensions of solar panels
Standard Dimensions of Solar Panels Understanding the Basics
As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy sources, solar power has gained substantial attention. One of the key components in solar energy systems is the solar panel, which converts sunlight into electricity. While solar panels come in various shapes and sizes, understanding the standard dimensions is crucial for consumers, manufacturers, and installers alike. This article will explore the typical dimensions of solar panels, their variations, and implications for installation.
Standard Sizes of Solar Panels
The universally accepted dimensions for solar panels largely depend on their type and the technology used in their manufacturing. The most common type of solar panel is the monocrystalline panel, which is known for its high efficiency and sleek design. The standard size for these panels is approximately 65 inches by 39 inches (1,650 mm x 1,000 mm). This size allows for a convenient balance between efficiency and space utilization.
Polycrystalline panels—the second most common type—are typically slightly larger, with standard dimensions of about 66 inches by 39 inches (1,680 mm x 1,000 mm). These panels are slightly less efficient than their monocrystalline counterparts, but they are more affordable due to their simpler manufacturing process.
For installations where space is a premium or for smaller applications, manufacturers also produce compact solar panels. These panels can be as small as 32 inches by 40 inches (810 mm x 1,020 mm), making them ideal for residential rooftops or areas with limited space. This flexibility in dimensions allows for tailored solutions depending on the specific requirements of the project.
Variations in Dimensions
standard dimensions of solar panels
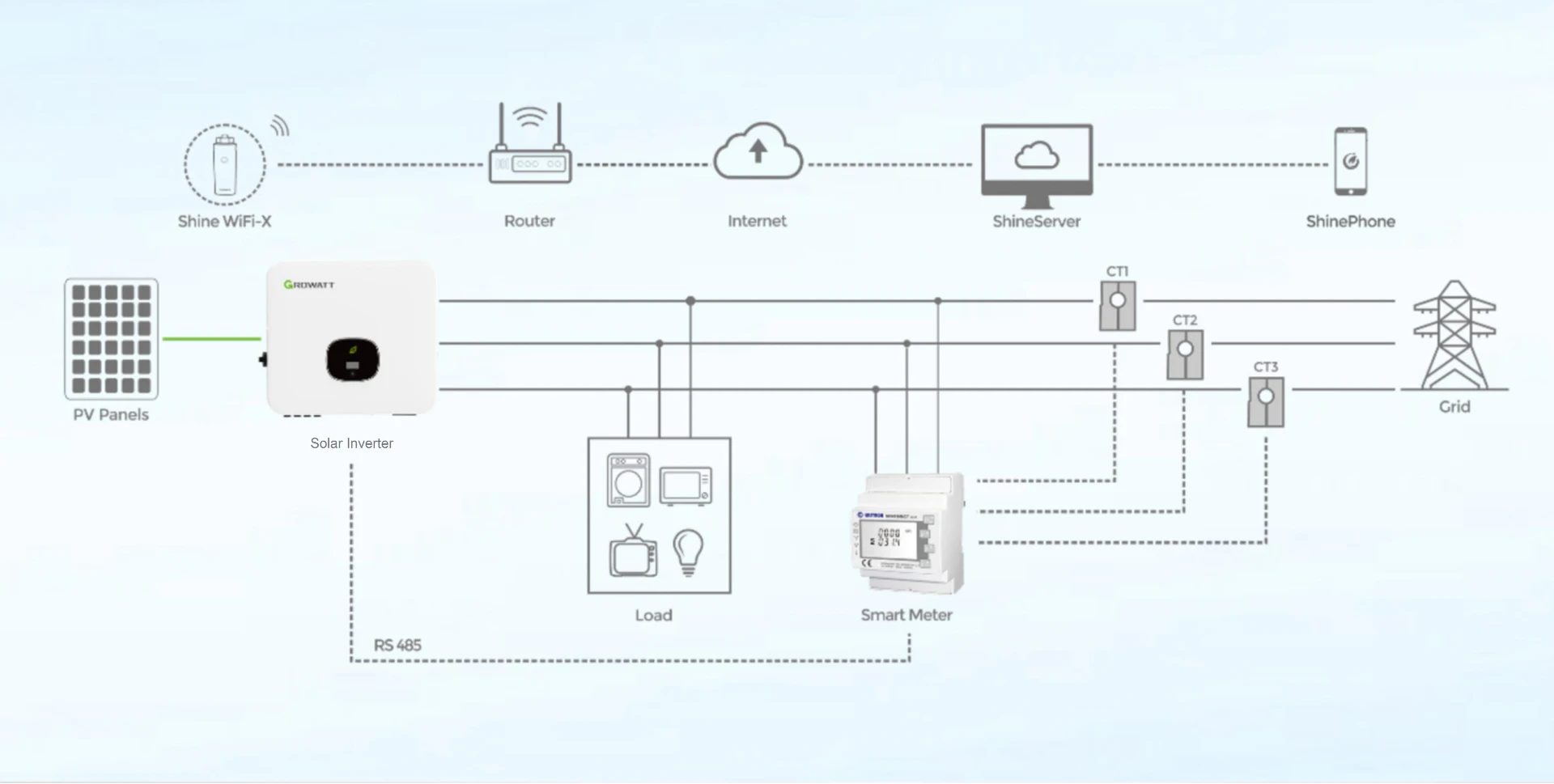
While the panel dimensions mentioned above are standard, it is essential to note that variations do exist. Different manufacturers may produce panels that deviate slightly in size, but typically, these differences do not exceed a few inches. The variation arises primarily from the design preferences and technologies employed by different manufacturers.
Additionally, advancements in technology lead to the development of specialized panels. Bifacial solar panels, which generate electricity from both sides, can have different dimensions and configurations than traditional panels. Similarly, thin-film solar panels, which are made by depositing photovoltaic materials onto a substrate, also differ in size and flexible design. While these panels are often less efficient, their lightweight and versatile attributes can open up new applications where traditional panels may not be suitable.
Implications for Installation
Understanding the dimensions of solar panels is crucial not only for procurement but also for installation. The size and weight of the panels can influence the type of mounting system used, the strength of the roofing structure, and the overall system design. For instance, larger panels may require more robust mounting solutions, which can increase installation costs and complexity.
Moreover, the total solar array's dimensions will affect the roof layout. Calculating the available space on a rooftop is essential to determine how many panels can be installed and how they should be oriented to optimize sunlight exposure. Proper planning can also help avoid shading from nearby structures and trees, which is crucial for maximizing energy production.
Conclusion
As solar energy continues to play a pivotal role in reducing reliance on fossil fuels, understanding the standard dimensions of solar panels is more important than ever. Consumers and installers must be aware of the various sizes available to make informed decisions that best suit their energy needs. While common panel dimensions standardize the market, technological advancements and variations ensure that there are flexible solutions to meet diverse application needs. By embracing these standards, we can work towards a more sustainable future powered by clean energy.
-
String Solar Inverter: The High-Efficiency Solution for Smart Solar EnergyNewsJul.14,2025
-
Revolutionizing Rooftop Energy with the Power of the Micro Solar InverterNewsJul.14,2025
-
Power Independence with Smart Off Grid Solar Inverter SolutionsNewsJul.14,2025
-
On Grid Solar Inverter: Powering the Future with Smart Grid IntegrationNewsJul.14,2025
-
Monocrystalline Solar Panels: High-Efficiency Power for the Future of Clean EnergyNewsJul.14,2025
-
Bifacial Solar Panel: A Smarter Investment for Next-Generation Energy SystemsNewsJul.14,2025







