Feb . 03, 2025 05:31
Back to list
JA 610-635W N-Type Bifacial Double Glass Mono Module Solar Panel
Solar panel plate size is a critical factor in the efficiency and implementation of solar energy systems. Understanding how the size of these solar panel plates affects performance, cost, and application is essential for making informed decisions. This article delves into the intricacies of solar panel plate sizes, drawing on extensive experience and industry expertise to provide authoritative and trustworthy insights.
Authoritative data from trusted industry analyses show that there's a growing trend towards using larger and more efficient solar panels. These advances often involve innovative manufacturing techniques that minimize the marginal increase in cost associated with scaling up panel size. However, one must weigh these potential benefits against the specific site limitations and long-term energy strategy. The environmental aspect also deserves attention. The increased materials and transportation implications for larger panels may affect their overall carbon footprint. Smaller panels, if utilized efficiently, can align better with eco-friendly building certifications and sustainability goals by facilitating optimized layout designs that reduce waste and maximize output. Understanding these nuances extends our expertise into practical applications. When designing a solar energy system, one must consider local solar irradiance levels, the pitch of the installation surface, and shading factors. Consulting with certified solar energy professionals offers the best chance of tailoring the system to effectively integrate the ideal solar panel size with its intended usage. In conclusion, choosing the right solar panel plate size requires a careful balance of multiple factors—energy needs, site conditions, budget, and sustainability considerations. Trustworthy counsel from experienced professionals and a precise exploration of market offerings are your best guides to making these important decisions. It's not just about selecting a solar panel; it's about planning an investment in a sustainable future that meets specific energy goals with maximum efficacy.

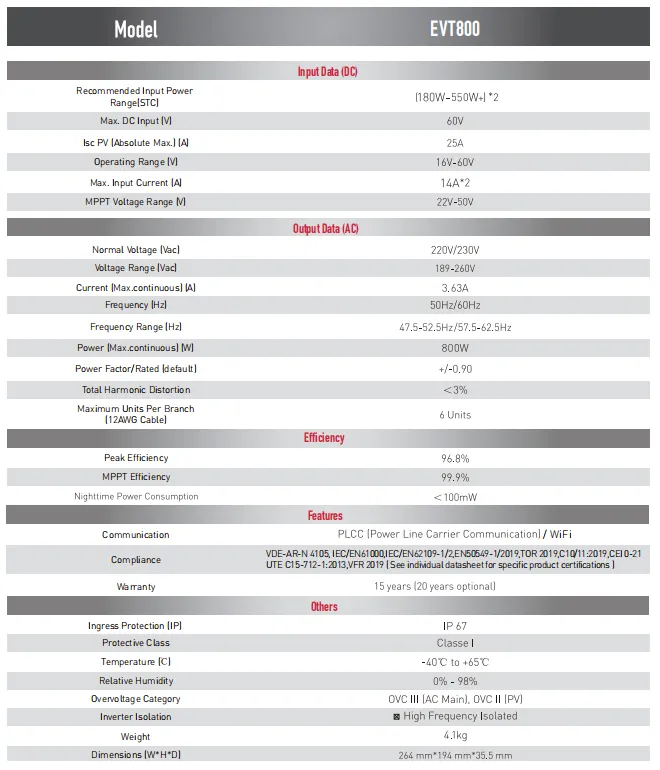
Authoritative data from trusted industry analyses show that there's a growing trend towards using larger and more efficient solar panels. These advances often involve innovative manufacturing techniques that minimize the marginal increase in cost associated with scaling up panel size. However, one must weigh these potential benefits against the specific site limitations and long-term energy strategy. The environmental aspect also deserves attention. The increased materials and transportation implications for larger panels may affect their overall carbon footprint. Smaller panels, if utilized efficiently, can align better with eco-friendly building certifications and sustainability goals by facilitating optimized layout designs that reduce waste and maximize output. Understanding these nuances extends our expertise into practical applications. When designing a solar energy system, one must consider local solar irradiance levels, the pitch of the installation surface, and shading factors. Consulting with certified solar energy professionals offers the best chance of tailoring the system to effectively integrate the ideal solar panel size with its intended usage. In conclusion, choosing the right solar panel plate size requires a careful balance of multiple factors—energy needs, site conditions, budget, and sustainability considerations. Trustworthy counsel from experienced professionals and a precise exploration of market offerings are your best guides to making these important decisions. It's not just about selecting a solar panel; it's about planning an investment in a sustainable future that meets specific energy goals with maximum efficacy.
Latest news
-
String Solar Inverter: The High-Efficiency Solution for Smart Solar EnergyNewsJul.14,2025
-
Revolutionizing Rooftop Energy with the Power of the Micro Solar InverterNewsJul.14,2025
-
Power Independence with Smart Off Grid Solar Inverter SolutionsNewsJul.14,2025
-
On Grid Solar Inverter: Powering the Future with Smart Grid IntegrationNewsJul.14,2025
-
Monocrystalline Solar Panels: High-Efficiency Power for the Future of Clean EnergyNewsJul.14,2025
-
Bifacial Solar Panel: A Smarter Investment for Next-Generation Energy SystemsNewsJul.14,2025
Related PRODUCTS







