house solar panels cost
The Cost of Solar Panels for Home Use A Comprehensive Overview
As the world increasingly shifts towards renewable energy sources, solar panels have emerged as a popular option for homeowners looking to reduce their carbon footprint while also cutting energy costs. However, one of the primary concerns for potential buyers is the cost associated with installing solar panels. This article aims to break down the various factors that contribute to the overall expense of home solar systems, provide average cost estimates, and discuss potential financial benefits.
Understanding the Initial Investment
The cost of solar panels for homes can vary widely based on several key elements, including the size of the system, the geographic location, the type of panels chosen, and the installation process. On average, homeowners can expect to spend between $15,000 and $25,000 for a complete solar panel system. This figure includes the solar panels themselves, inverters, mounting hardware, and installation labor. For a typical residential installation, the average cost per watt is around $2.50 to $3.50.
System Size and Energy Needs
The size of the solar panel system needed is primarily determined by your home's energy consumption. Most residential systems range from 4 kW to 10 kW, depending on the size of the home and the number of occupants. A larger system will naturally incur a higher cost. For instance, a 6 kW system could cost approximately $18,000, while a larger 10 kW system may cost around $25,000 or more. Conducting an energy audit can help you assess your specific needs and determine the size of the system that would be most beneficial.
Geographic Influence
Location plays a crucial role in the cost of solar panels. Areas with high solar insolation—meaning they receive a lot of sunlight throughout the year—are more favorable for solar panel installations. Conversely, regions that experience prolonged overcast conditions may find solar panels less effective and potentially less economically viable. Additionally, local labor rates, building codes, and permitting requirements can all influence installation costs. Therefore, it's essential to do some regional research to understand local pricing dynamics.
Types of Solar Panels
The type of solar panel you choose also significantly impacts the overall cost
. There are three main types of solar panelshouse solar panels cost
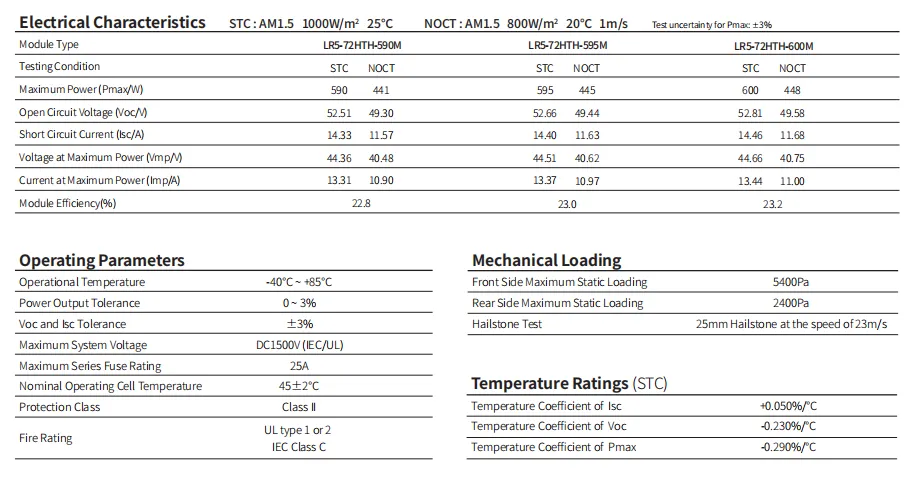
1. Monocrystalline Panels These panels are highly efficient and space-effective, but they typically come with a higher price tag, averaging around $1,000 to $3,000 for a 300-watt panel.
2. Polycrystalline Panels Slightly less efficient than monocrystalline, polycrystalline panels are generally more affordable, costing about $800 to $1,500 for a similar output.
3. Thin-Film Panels These panels are the least expensive and more lightweight, but they are also the least efficient. Their cost can range from $500 to $1,000 per 300-watt panel.
Choosing the right type of panel is vital, balancing initial costs against long-term energy savings.
Incentives and Rebates
One of the appealing aspects of investing in solar energy is the availability of opportunities for financial support. Many state and federal governments offer tax credits, rebates, and incentives that can significantly reduce the upfront costs of solar panel installations. For example, the Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) allows homeowners to deduct a certain percentage of the cost of installing a solar energy system from their federal taxes. As of 2023, this tax credit stands at 26%, providing substantial savings.
Long-Term Financial Returns
Investing in solar panels can lead to significant long-term savings on your energy bills. Homeowners can typically recoup their initial investment through savings on electricity costs within 5 to 10 years, depending on local energy prices and solar incentives. Additionally, solar panels can increase your home's value, making it an attractive option for future buyers.
Conclusion
While the upfront cost of solar panels for residential use can seem daunting, the long-term savings, environmental benefits, and available incentives make them an economical choice for many homeowners. By understanding the various factors that contribute to the cost and potential savings, you can make an informed decision about whether solar energy is right for your home. Transitioning to solar not only helps reduce dependence on nonrenewable energy sources but also contributes to a more sustainable future for all.
-
String Solar Inverter: The High-Efficiency Solution for Smart Solar EnergyNewsJul.14,2025
-
Revolutionizing Rooftop Energy with the Power of the Micro Solar InverterNewsJul.14,2025
-
Power Independence with Smart Off Grid Solar Inverter SolutionsNewsJul.14,2025
-
On Grid Solar Inverter: Powering the Future with Smart Grid IntegrationNewsJul.14,2025
-
Monocrystalline Solar Panels: High-Efficiency Power for the Future of Clean EnergyNewsJul.14,2025
-
Bifacial Solar Panel: A Smarter Investment for Next-Generation Energy SystemsNewsJul.14,2025







