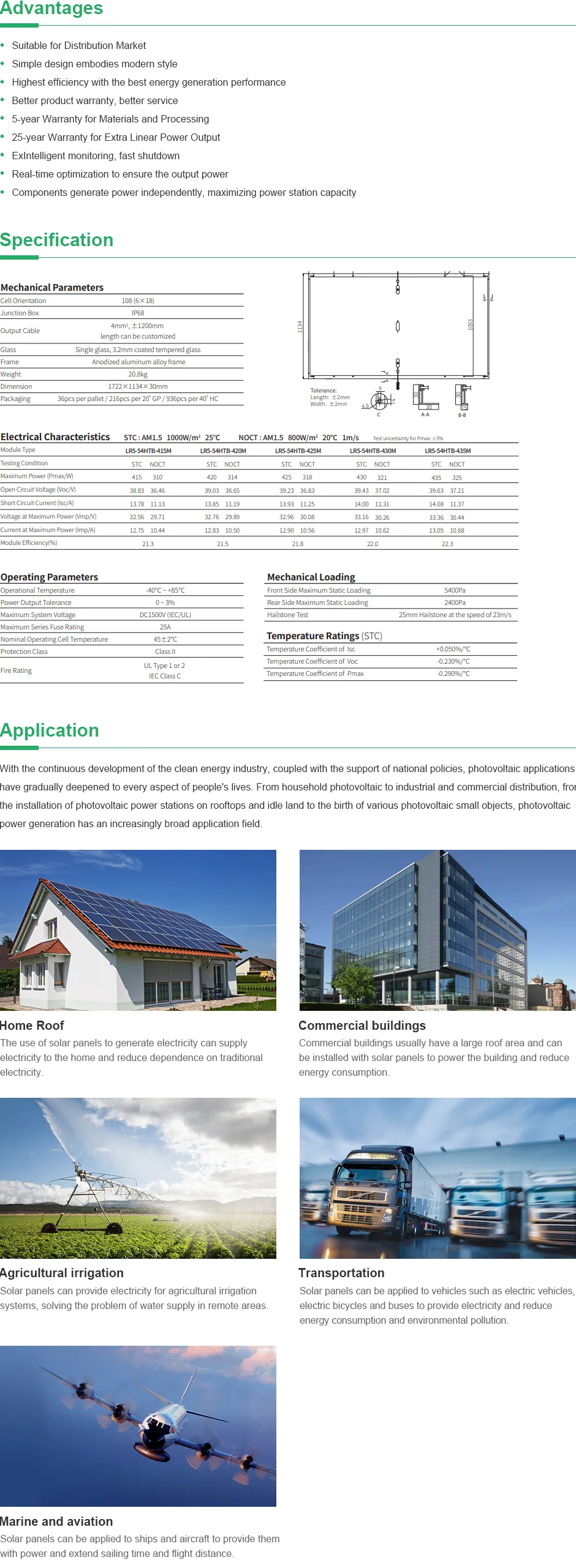
1kg watt solar panel price
Understanding the Price of 1 kg Watt Solar Panels
As the world moves towards sustainable energy solutions, solar panels have emerged as a popular choice for harnessing renewable energy. Among various types of solar panels, the price of solar panels is often assessed based on their capacity, and one common measure is the kilowatt (kW) per weight, often expressed in terms of 1 kg watt. Understanding the price dynamics of 1 kg watt solar panels can provide valuable insights for both consumers and investors looking to embrace solar technology.
What Is a Kilowatt Watt?
The term kilowatt refers to a unit of power equivalent to 1,000 watts. When discussing solar panels, this measure indicates the amount of electricity a panel can produce under optimal conditions. For instance, a 1 kW solar panel system can generate approximately 1,000 watts of electricity at peak performance.
The term 1 kg watt could be a slight misunderstanding; it is crucial to clarify that we typically discuss solar panels in kilowatts (kW) regarding their efficiency and production capability, not weight. Solar panels are usually rated in watts or kilowatts based on their energy output rather than their weight.
Factors Influencing Solar Panel Prices
When evaluating solar panel prices, multiple factors come into play
1. Technology The price of solar panels varies significantly based on the technology used. Monocrystalline panels, known for their higher efficiency and longevity, are typically more expensive than polycrystalline panels, which offer a lower price point but at the cost of efficiency.
2. Manufacturing Costs The cost of raw materials and manufacturing processes can influence prices. Innovations in production techniques may lead to cost reductions, making solar energy more accessible.
3. Supply Chain The fluctuating costs associated with the supply chain, including shipping and logistics, can impact the overall pricing of solar panels. Recent events, such as global supply chain disruptions due to the pandemic, have led to price increases in numerous industries, including solar energy.
1kg watt solar panel price
4. Government Incentives Many countries provide subsidies, tax incentives, and rebates for solar installation, which can significantly reduce the effective price of solar panels for consumers. Understanding these incentives can help consumers make informed purchasing decisions.
5. Market Dynamics Demand and competition within the solar panel market can affect pricing. As more companies enter the market, prices tend to stabilize or decrease, benefitting the consumer.
Current Pricing Overview
As of 2023, the average price for solar panels has been estimated between $200 to $350 per kilowatt installed, depending on the aforementioned factors. For a 1 kW solar panel system, this results in a price range of approximately $200 to $350 before any incentives or credits are applied. However, when considering the price per weight, these panels are generally designed to be lightweight for ease of installation, averaging around 15-20 kg for a typical residential panel.
Future Considerations
Investing in solar panels is not only about the initial cost; it’s also about long-term savings on electricity bills and reducing carbon footprints. As technology advances, we can expect further reductions in prices and increased efficiency in solar panels.
Furthermore, the ongoing global push towards renewable energy sources signifies a promising market for solar panels. Understanding the intricacies of solar panel pricing, such as the significance of kilowatts and market dynamics, can aid consumers in their transition to renewable energy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the price of solar panels, particularly when considering their kilowatt output, involves several critical factors, including technology type, manufacturing costs, and market dynamics. For those interested in purchasing solar energy systems, it's essential to stay informed and evaluate all available options, including financial incentives that may make solar power more accessible and affordable. As we continue to advance towards a greener future, understanding the financial implications of solar energy will become increasingly important for consumers and investors alike.
-
String Solar Inverter: The High-Efficiency Solution for Smart Solar EnergyNewsJul.14,2025
-
Revolutionizing Rooftop Energy with the Power of the Micro Solar InverterNewsJul.14,2025
-
Power Independence with Smart Off Grid Solar Inverter SolutionsNewsJul.14,2025
-
On Grid Solar Inverter: Powering the Future with Smart Grid IntegrationNewsJul.14,2025
-
Monocrystalline Solar Panels: High-Efficiency Power for the Future of Clean EnergyNewsJul.14,2025
-
Bifacial Solar Panel: A Smarter Investment for Next-Generation Energy SystemsNewsJul.14,2025







