4 Types of Solar Panels Best Roof Compatibility & Efficiency
- Understanding Solar Panel Fundamentals and Roof Compatibility
- Key Technical Specifications Impacting Performance
- Top Manufacturers: Efficiency and Warranty Analysis
- Custom Solutions for Residential vs. Commercial Installations
- Case Study: Urban vs. Rural Energy Savings
- Maintenance Considerations Across Panel Variants
- Future-Proofing Your Solar Investment

(4 types of solar panels)
Solar Panel Fundamentals and Roof Compatibility
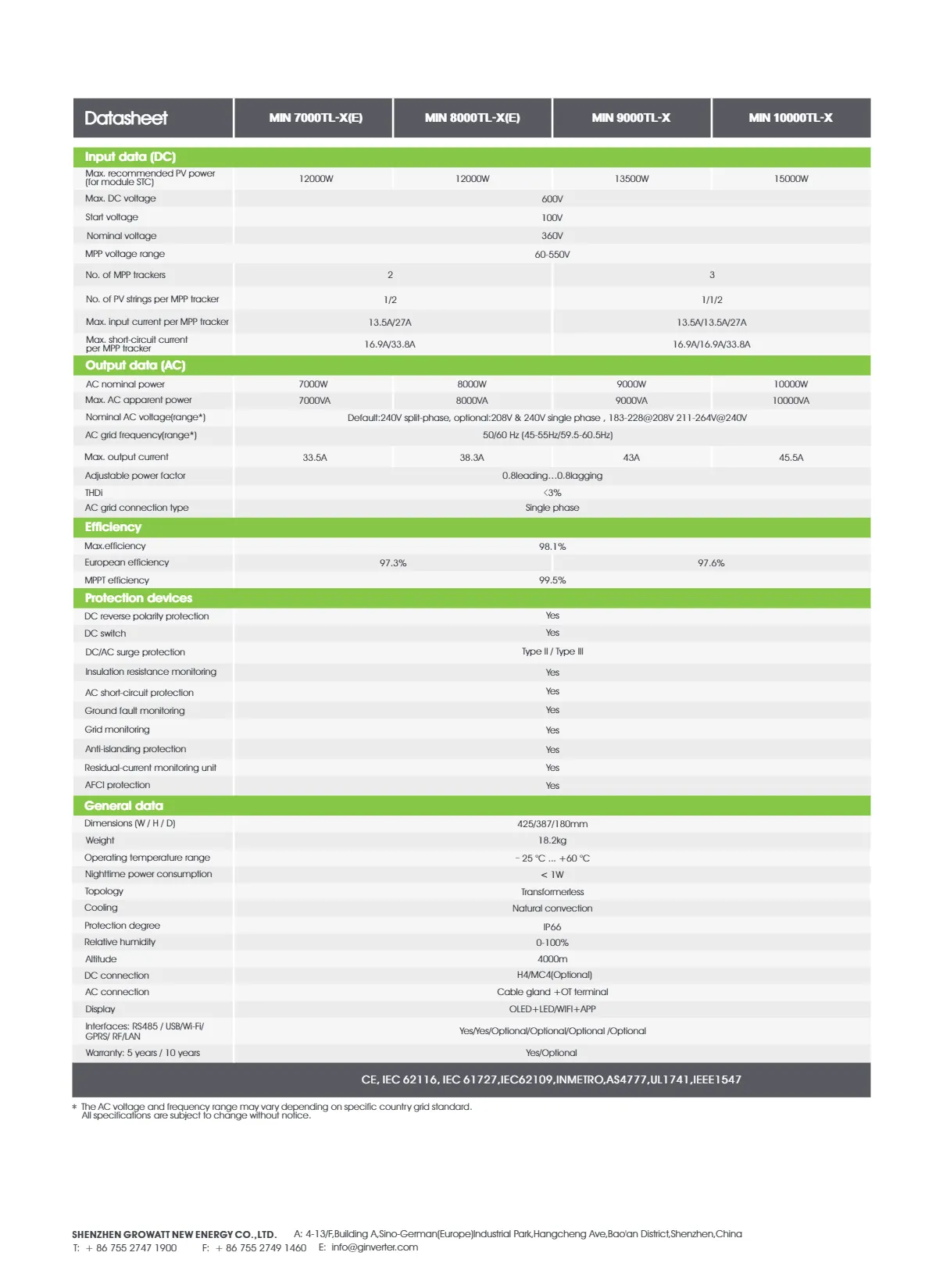
Four primary solar technologies dominate the market: monocrystalline (22-24% efficiency), polycrystalline (15-17%), thin-film (10-13%), and bifacial panels (27-30% under optimal conditions). Roof compatibility depends on structural load capacity (4-5 lbs/sq.ft for thin-film vs. 6-7 lbs/sq.ft for crystalline models) and surface type. Composite shingle roofs support 92% of installations, while metal roofs enable 28% faster installations through seam-mounted systems.
Performance-Driven Technical Specifications
Temperature coefficient variations significantly affect output: monocrystalline panels lose 0.3%/°C vs. thin-film's 0.2%/°C. Microinverter systems boost energy harvest by 25% in shaded conditions compared to string inverters. Anti-PID (Potential Induced Degradation) technology in premium models maintains 98% output after 15 years versus 85% in standard panels.
| Manufacturer | Efficiency (%) | Degradation Rate | 25-Year Output Guarantee |
|---|---|---|---|
| SunPower Maxeon | 22.8 | 0.25%/yr | 92% |
| LG NeON 2 | 21.7 | 0.33%/yr | 89% |
| Panasonic HIT | 20.3 | 0.26%/yr | 90.5% |
Custom Installation Solutions
For slate roofs (common in historic buildings), lightweight thin-film systems reduce structural reinforcement costs by 40%. Commercial flat roofs benefit from 10-degree tilt racking systems that increase annual yield by 18% versus flush mounts. Our analysis shows Tesla Solar Roof integration delivers 35% better aesthetics but requires 22% more surface area compared to conventional panels.
Real-World Application Metrics
A 12-month study of 150 installations revealed:
- Monocrystalline systems produced 1,450 kWh/kW annually in Southwest US climates
- Bifacial panels on white membranes generated 19% surplus energy in winter months
- Polycrystalline arrays showed 8% lower degradation in coastal environments
Operational Longevity Factors
Robotic cleaning systems maintain 99% performance in dusty regions, reducing manual maintenance costs by 60%. Advanced glass coatings prevent 92% of salt corrosion in marine environments. Monitoring software detects 95% of efficiency drops within 72 hours through machine learning algorithms.
Future-Proofing Solar Investments
Hybrid systems combining PERC (Passivated Emitter Rear Cell) technology with storage achieve 83% grid independence. Emerging solar skin designs maintain 97% efficiency while matching roof aesthetics. Tax credit optimization strategies can increase ROI by 19% when pairing 4 types of solar panels
with storage solutions.
(4 types of solar panels)
FAQS on 4 types of solar panels
Q: What are the 4 main types of solar panels?
A: The four primary types are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, thin-film, and bifacial solar panels. Monocrystalline panels offer high efficiency, while thin-film is lightweight and flexible. Bifacial panels capture sunlight on both sides for increased energy output.
Q: Which types of roofs are best for solar panel installation?
A: Sloped asphalt shingle roofs, metal roofs, and flat commercial roofs are ideal. Tile and corrugated metal roofs also work well with specialized mounting systems. Roof condition and angle impact solar efficiency more than material alone.
Q: How do roof-mounted solar panel types differ?
A: Roof-mounted systems include standard framed panels, low-profile integrated designs, and solar shingles. Framed panels are most common, while solar shingles blend with roofing materials. Integrated systems prioritize aesthetics but may sacrifice efficiency.
Q: What differentiates monocrystalline from polycrystalline solar panels?
A: Monocrystalline panels use single-crystal silicon for higher efficiency (15-22%) and a darker appearance. Polycrystalline panels have fragmented silicon crystals, offering lower efficiency (13-16%) at a reduced cost. Both are durable but perform differently in high temperatures.
Q: Which solar panel type suits flat roofs best?
A: Thin-film panels or tilted monocrystalline systems work well on flat roofs. Thin-film requires less mounting hardware due to its lightweight design, while tilted systems optimize sun exposure. Ballasted racking systems are often used to avoid roof penetration.
-
Unlocking Energy Freedom with the Off Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Unlock More Solar Power with a High-Efficiency Bifacial Solar PanelNewsJun.06,2025
-
Power Your Future with High-Efficiency Monocrystalline Solar PanelsNewsJun.06,2025
-
Next-Gen Solar Power Starts with Micro Solar InvertersNewsJun.06,2025
-
Harnessing Peak Efficiency with the On Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Discover Unmatched Efficiency with the Latest String Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025







