panel bifacial vs monofacial
Bifacial vs. Monofacial Solar Panels A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of solar technology, the choice between bifacial and monofacial solar panels represents a significant decision for solar installers and consumers alike. Both technologies offer unique advantages and address distinct market needs. To understand the implications of choosing one over the other, a detailed comparison is warranted.
Overview of Solar Panel Technology
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic (PV) cells. Monofacial panels, the more traditional option, have solar cells on one side only, while bifacial panels can capture sunlight from both their front and rear surfaces. This fundamental difference contributes to various operational efficiencies and applications suited for each type.
Efficiency and Performance
One of the primary advantages of bifacial solar panels is their enhanced efficiency. Because they harness light from both sides, bifacial panels can achieve higher energy yields, particularly in albedo-rich environments where light reflects off surfaces like snow, water, or sand. Studies indicate that bifacial panels can produce up to 30% more energy than their monofacial counterparts under optimal conditions. This leads to more substantial energy production over the panels’ lifespan, which typically spans 25 years or more.
Monofacial panels, on the other hand, offer reliable performance and have a proven track record. They are simpler in design, which often makes them less expensive. However, their efficiency can plateau, especially in environments with low reflectivity. Thus, while monofacial panels are widely deployed and understood, they may not perform as well in certain conditions compared to bifacial ones.
Installation Considerations
The installation process for bifacial solar panels can be more demanding. These panels require that the installation site maximizes ground reflection to benefit from their two-sided design. This can translate into higher installation costs and necessitates careful site selection.
panel bifacial vs monofacial
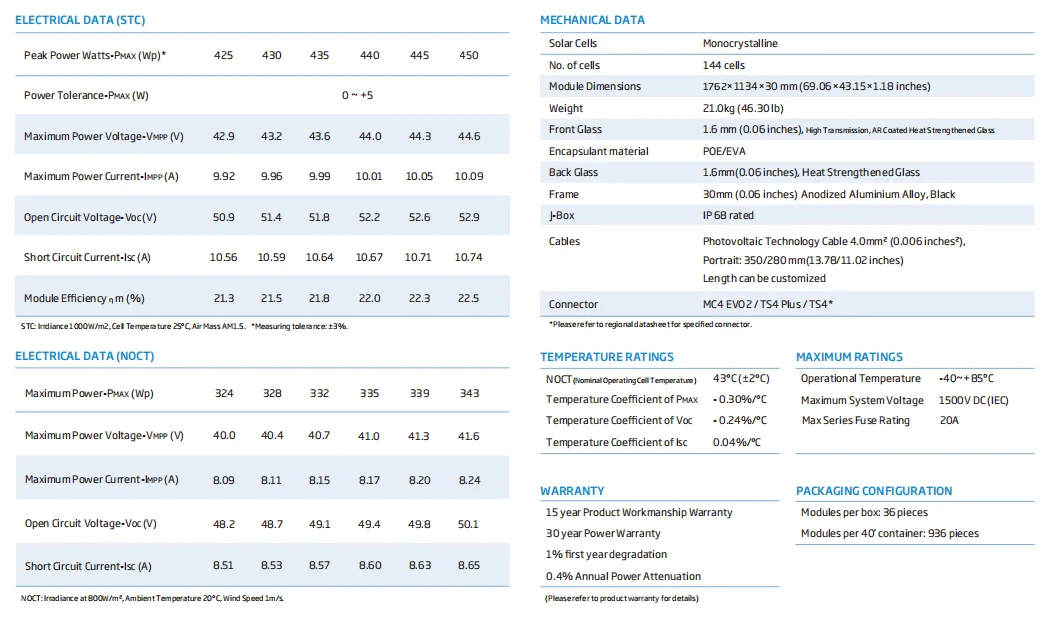
In contrast, monofacial panels are typically easier to install and can be placed in a broader range of locations without special considerations for reflected light. This flexibility is especially appealing for residential installations and projects where costs are a critical factor.
Cost Implications
Cost is one of the most significant decision-making factors in the choice between bifacial and monofacial panels. Bifacial panels generally have higher upfront costs, owing to their sophisticated design and the necessity for additional mounting solutions that can effectively capture reflected light. However, the increased energy yield might justify the higher initial investment over time.
Monofacial panels remain a popular choice due to their lower initial costs and established performance. For consumers particularly focused on budget constraints or those seeking to install solar solutions in less-than-ideal locations, monofacial panels may provide a more straightforward route to energy independence.
Applications and Suitability
The choice between bifacial and monofacial also hinges on the specific application. Bifacial panels are particularly suited for utility-scale solar farms, where maximizing output is essential. They are also preferable in locations where land use is optimized—such as agrivoltaics, where crops can grow beneath the panels, and sunlight can be utilized from both sides.
Conversely, monofacial panels are often the go-to solution for residential installations or small commercial projects due to their established ease of use and effective performance in various environmental conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bifacial and monofacial solar panels each present compelling advantages and varying degrees of suitability depending on the installation context. Bifacial panels offer greater efficiency and energy production in specific environments, while monofacial panels are championed for their cost-effectiveness and simplicity. Ultimately, the decision between bifacial and monofacial panels should be guided by the specific energy needs, installation conditions, and budget considerations of the project at hand. By carefully weighing these factors, consumers and installers can align their solar solutions with their energy goals for a sustainable future.
-
Unlocking Energy Freedom with the Off Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Unlock More Solar Power with a High-Efficiency Bifacial Solar PanelNewsJun.06,2025
-
Power Your Future with High-Efficiency Monocrystalline Solar PanelsNewsJun.06,2025
-
Next-Gen Solar Power Starts with Micro Solar InvertersNewsJun.06,2025
-
Harnessing Peak Efficiency with the On Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Discover Unmatched Efficiency with the Latest String Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025







