Innovative Research on Solar Panel Projects for Sustainable Energy Solutions and Environmental Impact
Understanding Solar Panel Projects Harnessing the Power of the Sun
In recent years, the importance of renewable energy sources has become increasingly evident as we face the looming threat of climate change and the depletion of fossil fuels. Among various renewable energy technologies, solar panels have emerged as one of the most promising solutions for sustainable energy generation. This article delves into the science behind solar panel projects, their components, functioning, benefits, and challenges, ultimately highlighting their significant role in promoting a greener future.
The Science of Solar Energy
At its core, solar energy relies on the photovoltaic effect, a process through which sunlight is converted into electricity. This effect occurs in materials called semiconductors, primarily silicon. When sunlight (photons) strikes a silicon-based solar cell, it energizes the electrons within the semiconductor material, allowing them to flow and create an electric current. This current can then be harnessed and converted into usable electricity, which can power homes, businesses, and even electric vehicles.
Components of a Solar Panel System
A typical solar panel project consists of several key components
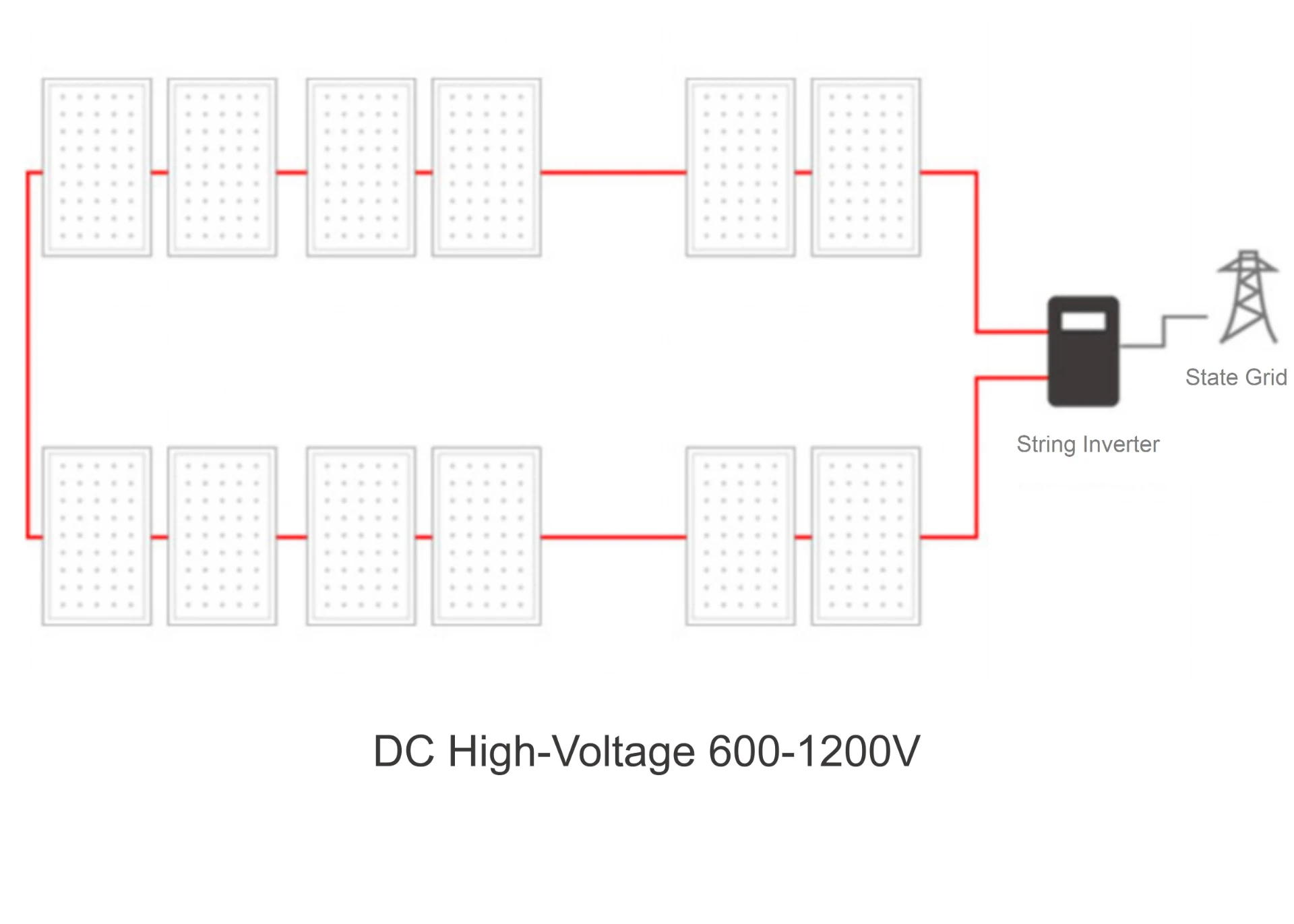
1. Solar Panels The most visible part of the system, comprising solar cells made from silicon or other semiconductor materials. These panels convert sunlight into electricity.
2. Inverter This device plays a critical role in solar energy systems. It converts the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is the standard form of electricity used in homes and businesses.
3. Mounting Structures These are necessary to securely attach the solar panels to rooftops or the ground, ensuring they are positioned at the optimal angle to capture sunlight.
4. Battery Storage Some solar panel projects incorporate battery systems that store excess electricity generated during sunny periods. This stored energy can be used during cloudy days or at night, providing a reliable power supply.
5. Monitoring Systems To maximize efficiency and performance, many solar projects include monitoring systems that track energy production, usage, and potential issues with the system.
Benefits of Solar Panel Projects
solar panel project science
1. Environmental Impact Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource that reduces greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants. By harnessing sunlight, solar panel projects mitigate climate change and contribute to cleaner air.
2. Energy Independence Solar panel projects reduce reliance on fossil fuels, enhancing energy security for individuals and nations. By generating their own electricity, homeowners and businesses can decrease their vulnerability to energy price fluctuations.
3. Economic Opportunities The growth of solar energy technology has spurred job creation in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance sectors, fostering local economies.
4. Low Operating Costs After the initial investment in solar panels and installation, the ongoing maintenance costs are relatively low. Solar energy systems can significantly reduce electricity bills over time, offering substantial savings.
Challenges Facing Solar Panel Projects
Despite the numerous advantages, several challenges persist in the widespread adoption of solar energy
1. Initial Costs The upfront investment required for solar panel installation can be a barrier for many homeowners and businesses. However, advances in technology and increased competition in the market are gradually reducing these costs.
2. Intermittent Energy Supply Solar energy generation is dependent on sunlight, which can be inconsistent due to weather conditions or time of day. This intermittency can be addressed through battery storage systems or integration with other renewable energy sources to provide a more reliable energy supply.
3. Land Use Large-scale solar projects require significant land areas, which can raise concerns regarding land use and habitat disruption. The development of solar farms must be carefully planned to minimize ecological impacts.
4. Resource Limitations The production of solar panels requires raw materials such as silicon and rare metals. Ensuring a sustainable supply chain is vital for the long-term viability of solar technology.
Conclusion
Solar panel projects represent a cornerstone of the transition to renewable energy, driven by science and innovation. By converting sunlight into electricity, solar energy offers a sustainable solution to some of the most pressing environmental challenges we face today. While challenges exist, the benefits of solar panels in promoting energy independence, environmental sustainability, and economic growth cannot be overstated. As technology continues to advance and awareness of climate issues grows, the future of solar energy looks increasingly bright.
-
Unlocking Energy Freedom with the Off Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Unlock More Solar Power with a High-Efficiency Bifacial Solar PanelNewsJun.06,2025
-
Power Your Future with High-Efficiency Monocrystalline Solar PanelsNewsJun.06,2025
-
Next-Gen Solar Power Starts with Micro Solar InvertersNewsJun.06,2025
-
Harnessing Peak Efficiency with the On Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Discover Unmatched Efficiency with the Latest String Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025







