Harnessing Solar Energy for Industrial Self-Sufficiency: The Power of On-Grid Solar Inverters
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, businesses are increasingly turning to sustainable energy solutions to reduce costs and enhance their environmental footprint. One of the most effective ways to achieve energy self-sufficiency is through the use of on-grid solar inverters. These advanced systems help large industrial facilities generate their own electricity from solar energy, while also allowing for seamless integration with the existing grid. In this article, we will dive into the role of grid-connected inverters in industrial applications and explore how they contribute to energy independence.
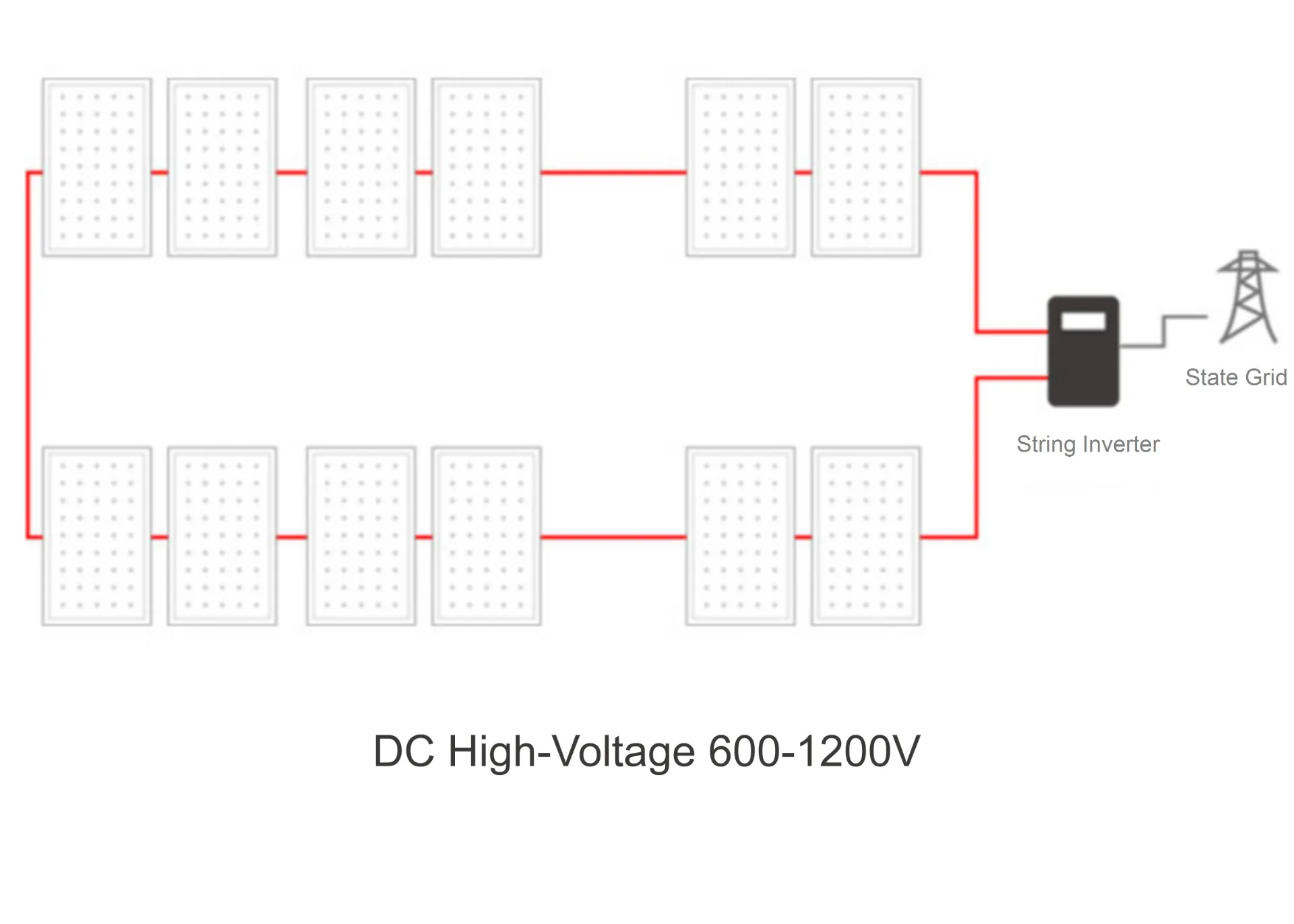
What is an On-Grid Solar Inverter and How Does It Work?
An on-grid solar inverter, also known as a tie grid inverter or grid-connected inverter, is a system designed to convert the DC (Direct Current) electricity generated by solar panels into AC (Alternating Current) electricity, which is compatible with the electrical grid. The primary function of an on-grid inverter is to allow the solar energy generated by the panels to be used directly by the industrial facility or fed back into the public grid. This process helps facilities reduce their reliance on traditional power sources, leading to cost savings and a more sustainable energy profile.
그만큼 on-grid inverter ensures that the electricity generated by the solar panels is synchronized with the grid’s frequency, enabling the flow of electricity between the two systems. These inverters come equipped with safety features to protect both the solar array and the utility grid from issues like overvoltage or grid instability. This functionality is key to maintaining operational stability and maximizing the efficiency of the solar energy system.
The Role of Tie Grid Inverters in Achieving Energy Self-Sufficiency
For large industrial facilities, tie grid inverters play a crucial role in the quest for energy self-sufficiency. Unlike off-grid systems, which rely solely on stored energy in batteries, tie grid inverters allow for continuous access to electricity while minimizing dependency on external energy sources. This capability is especially valuable for industries that operate around the clock, where energy consumption is high and consistency is vital.
By connecting directly to the grid, tie grid inverters provide the flexibility to both consume and produce electricity, creating a dynamic, two-way energy exchange. When the facility’s solar system generates more electricity than needed, the excess can be fed back into the grid, potentially earning the business credits or compensation from the utility provider. Similarly, if the solar output falls short during periods of low sunlight, the business can pull electricity from the grid to meet its needs without disruption.
This integration helps large industrial facilities achieve energy self-sufficiency, significantly reducing reliance on traditional, non-renewable energy sources while contributing to sustainability goals.
Micro Tie Grid Inverters: A Flexible Solution for Smaller Industrial Applications
In addition to traditional on-grid solar inverters, some industrial applications benefit from the use of micro tie grid inverters. These inverters are designed for smaller-scale solar installations, offering an adaptable solution for facilities that may not require a large, centralized system.
Micro tie grid inverters are often installed on each individual solar panel, allowing for maximum efficiency and flexibility in the energy generation process. Unlike conventional systems where the entire array operates as a single unit, each panel with a micro inverter operates independently. This decentralized approach ensures that any issues with one panel—such as shading or dirt buildup—don’t affect the performance of the entire system. Furthermore, it enables optimal power output from each panel, leading to greater energy production and better overall system efficiency.
For industrial facilities that operate in spaces with variable roof orientations or partial shading, micro tie grid inverters provide a more efficient and flexible solution for achieving energy self-sufficiency.
Tie Inverter Grid: Key Advantages for Industrial Energy Management
The term tie inverter grid refers to the overall integration of solar inverters with the utility grid, creating a seamless connection between renewable energy sources and public electricity systems. This setup allows industrial facilities to continuously optimize their energy use by balancing solar energy production with the need for grid power.
Tie inverter grids provide several key advantages for industrial applications, including:
Cost Savings: By reducing reliance on grid power during peak hours, businesses can lower their electricity bills. In some regions, businesses can also earn credits or rebates for surplus energy sent back to the grid.
Enhanced Energy Security: Facilities with tie inverter grids are less vulnerable to grid outages or fluctuations. The ability to produce their own energy ensures business continuity, even during external power disruptions.
Scalability: As energy demand increases, industrial facilities can easily scale up their solar installations. The tie inverter grid system can be expanded with additional solar panels and inverters, ensuring that the business continues to meet its energy needs without significantly increasing overhead costs.
Sustainability: Tie inverter grids allow industrial facilities to minimize their carbon footprint by shifting towards renewable energy sources. By reducing dependency on fossil fuels and utilizing solar energy, businesses can meet sustainability goals while contributing to cleaner air and water.
The future of on-grid solar inverters looks promising, with ongoing innovations in energy technology, such as smart grid integration, energy storage solutions, and advanced inverter features. As industries continue to seek more sustainable energy solutions, on-grid solar inverters will play a pivotal role in transitioning towards fully renewable, self-sufficient energy systems.
Emerging trends include:
Advanced Monitoring and Control Systems: Future on-grid solar inverters will likely feature enhanced smart capabilities, allowing facilities to monitor and control their energy usage more precisely. This includes real-time data on energy production, consumption, and system health.
Battery Storage Integration: While on-grid inverters already enable the export of excess energy to the grid, the integration of energy storage systems will allow facilities to store surplus energy for use during periods of low production or high demand.
Optimized Efficiency: As demand for energy-efficient systems increases, on-grid solar inverters will continue to evolve to maximize the energy harvested from the sun, further driving down operational costs.
For large industrial facilities looking to achieve energy self-sufficiency, investing in on-grid solar inverters is not just a step toward reducing electricity costs, but also a significant move toward a greener, more sustainable future. Whether choosing traditional tie grid inverters, micro tie grid inverters, or exploring the potential of tie inverter grid systems, these solutions will play a crucial role in shaping the future of industrial energy management.
-
Navigating Off Grid Solar Inverter: From Use Cases to Trusted Partners소식Aug.05,2025
-
Solar Edge String Inverter: A Wholesaler’s Guide to Inverter Technology Selection소식Aug.05,2025
-
Microinverters: Revolutionizing Solar Energy Use소식Aug.05,2025
-
Future of Monocrystalline Solar Panel Efficiency: Latest Technological Advances소식Aug.05,2025
-
Solar Panels for House: A Complete Guide to Residential Solar Energy소식Aug.05,2025
-
Panel Bifacial Performance in Snow and Low-Light Conditions소식Aug.05,2025







