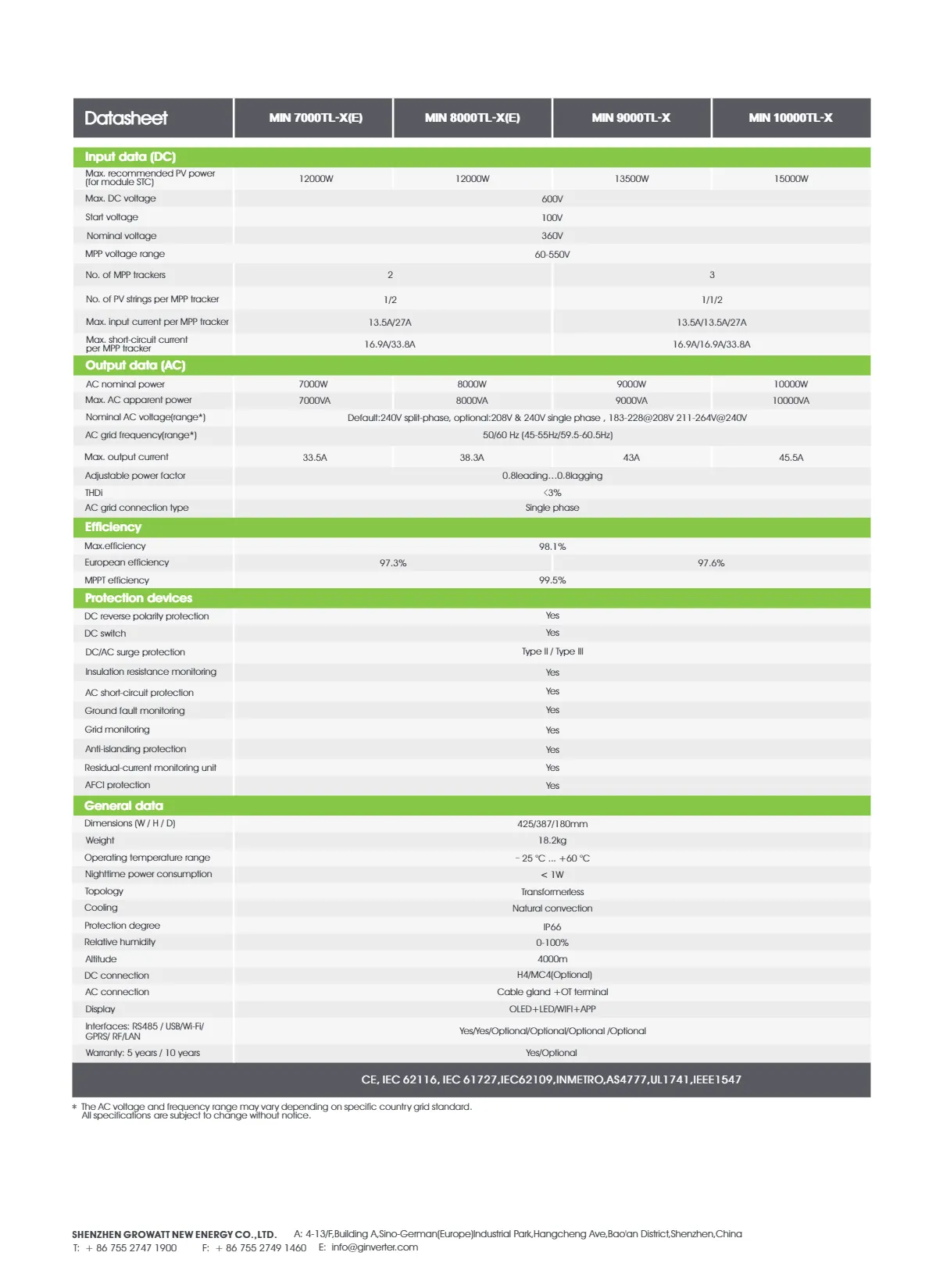
solar pv
Understanding Solar Photovoltaics Benefits and Challenges
As the world pivots toward sustainable energy sources, solar photovoltaics (PV) have emerged as a pivotal technology in the renewable energy landscape. Solar PV refers to the conversion of sunlight into electricity using semiconductor materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect. This article explores the principles of solar PV, its benefits, challenges, and its role in the transition to a cleaner energy future.
The Principles of Solar Photovoltaics
Solar PV systems consist of solar panels, which are made up of numerous solar cells. Each solar cell typically comprises silicon, a semiconductor material that can efficiently convert sunlight into electricity. When sunlight hits these cells, it excites electrons, creating an electric current. This process can be summarized in a few basic steps
1. Absorption of Sunlight Sunlight, made up of photons, strikes the surface of a solar panel. 2. Electron Excitation The energy from the absorbed photons excites electrons in the silicon, freeing them from atoms.
3. Current Generation The movement of these free electrons creates a flow of electric current. This direct current (DC) can then be converted to alternating current (AC) through an inverter, making it usable for homes and businesses.
Benefits of Solar PV
1. Renewable Energy Source Solar energy is abundant and inexhaustible. Unlike fossil fuels, which deplete over time, the sun provides a continuous supply of energy.
2. Environmental Impact Solar PV systems generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, which helps combat climate change and reduce air pollution. By incorporating solar energy into the energy mix, societies can lower their carbon footprint significantly.
3. Economic Advantages The cost of solar technology has fallen dramatically over the past decade. This decrease in costs has made solar PV an attractive investment for both residential and commercial properties. Moreover, solar installations create jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, contributing to local economies.
solar pv
4. Energy Independence By harnessing solar energy, countries can reduce their reliance on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security. This shift can stabilize energy prices and protect economies from geopolitical tensions related to energy supplies.
5. Versatility and Scalability Solar PV systems can be deployed in various settings, from small-scale residential rooftops to large utility-scale solar farms. This versatility allows for tailored solutions that meet specific energy needs.
Challenges Facing Solar PV
Despite its many benefits, solar PV technology does face several challenges that need addressing
1. Intermittency Solar energy production is dependent on sunlight, which fluctuates throughout the day and is affected by weather conditions. This intermittency can pose challenges for electricity grids, necessitating the development of better energy storage solutions or backup systems.
2. Land Use Large-scale solar farms require significant land, which can impact local ecosystems and land availability for agriculture. Thoughtful planning and site selection are crucial to mitigate potential negative effects.
3. End-of-Life Management The disposal of solar panels raises environmental concerns. Although many materials in solar panels are recyclable, the processes for efficient recycling are still developing. Proper waste management policies will be essential as the installed base of solar panels grows.
4. Initial Costs While the costs of solar technology have decreased, the upfront investment for residential solar systems can still be a barrier for some homeowners. Innovative financing models, incentives, and subsidies can help make solar installations accessible to broader audiences.
Conclusion
Solar photovoltaics stand at the forefront of the transition to renewable energy, offering a wide array of benefits that can significantly contribute to a sustainable future. However, realizing the full potential of solar PV requires overcoming several challenges, including intermittency, land use, and end-of-life management. As technology advances and policies evolve, solar energy will undoubtedly play a crucial role in achieving global sustainability goals, fostering a cleaner, greener planet for future generations. With ongoing research, innovation, and a collective commitment to renewable energy, the prospects for solar PV remain bright.
-
Navigating Off Grid Solar Inverter: From Use Cases to Trusted PartnersNewsAug.05,2025
-
Solar Edge String Inverter: A Wholesaler’s Guide to Inverter Technology SelectionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Microinverters: Revolutionizing Solar Energy UseNewsAug.05,2025
-
Future of Monocrystalline Solar Panel Efficiency: Latest Technological AdvancesNewsAug.05,2025
-
Solar Panels for House: A Complete Guide to Residential Solar EnergyNewsAug.05,2025
-
Panel Bifacial Performance in Snow and Low-Light ConditionsNewsAug.05,2025







