Comparing Monofacial and Bifacial Solar Panels for Optimal Energy Efficiency
Monofacial vs. Bifacial Solar Panels A Comparative Analysis
As the world shifts towards renewable energy sources, solar power continues to play a pivotal role in reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainability. Within the solar industry, two primary types of solar panels have emerged monofacial and bifacial solar panels. Understanding the differences between these technologies is crucial for homeowners, businesses, and investors looking to make informed decisions about solar energy systems.
Monofacial Solar Panels
Monofacial solar panels are the traditional solar panels most commonly used in residential and commercial installations. These panels have solar cells on one side and are usually mounted on a frame that is oriented towards the sun. The efficiency of monofacial panels generally ranges from 15% to 20%, depending on the technology used and the quality of the cells.
One significant advantage of monofacial panels is their lower initial cost. They are simpler to manufacture and typically have a lower price point compared to bifacial panels. This makes them an attractive option for individuals and businesses seeking to adopt solar technology without making a hefty financial commitment upfront.
However, one of the primary limitations of monofacial panels is their dependence on direct sunlight. These panels can only generate electricity from the sunlight that directly hits their surface. Consequently, their performance can be significantly impacted by shading from trees, buildings, or cloud cover. In addition, the orientation and inclination of these panels play a crucial role in maximizing their energy output.
Bifacial Solar Panels
monofacial vs bifacial solar
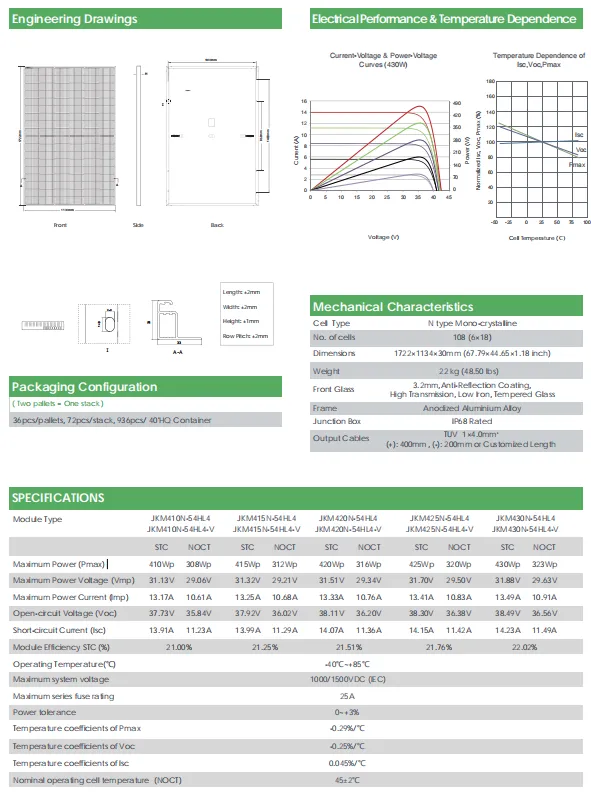
Bifacial solar panels, on the other hand, represent a more advanced technology that allows energy generation from both sides of the panel. This design typically utilizes transparent materials on the back, allowing sunlight to be reflected from the ground or surrounding surfaces to reach the rear side of the panel. As a result, bifacial panels can harness additional energy, notably in environments with reflective surfaces such as snow, sand, or light-colored concrete.
The efficiency of bifacial panels can exceed that of monofacial panels, particularly when installed in optimal conditions. They can generate up to 30% more energy compared to traditional panels, depending on site conditions and reflectivity. This feature makes bifacial panels a compelling choice for utility-scale solar projects and installations in areas with high albedo.
Despite their efficiency and potential for higher energy yield, bifacial panels typically come with a higher initial investment. The manufacturing process is more complex, which contributes to increased costs. However, the long-term benefits of higher energy output can often offset the initial expense, making them an attractive option for large-scale installations.
Conclusion
When determining whether to invest in monofacial or bifacial solar panels, stakeholders must consider a variety of factors. Monofacial panels offer a reliable and cost-effective solution for residential and small-scale applications, while bifacial panels present an opportunity for increased efficiency in favorable conditions, particularly for large-scale installations.
Ultimately, the choice between monofacial and bifacial solar panels will depend on specific project goals, budget constraints, and site conditions. As technology continues to evolve and the demand for renewable energy sources increases, understanding the nuances of these two types of solar panels will be vital for making an informed decision, ensuring an effective and sustainable investment in solar energy.
-
Understanding the Advantages of Solar String Inverters for Your Energy SystemNewsApr.29,2025
-
Choosing the Right PV Inverter: A Comprehensive GuideNewsApr.29,2025
-
The Future of Solar Power: Exploring Bifacial Solar PanelsNewsApr.29,2025
-
The Complete Guide to Solar Panels: Efficiency, Cost, And InstallationNewsApr.29,2025
-
The Best Options for Efficiency and Cost-EffectivenessNewsApr.29,2025
-
Harnessing the Power of Off-Grid Solar Inverters for Energy IndependenceNewsApr.29,2025







