High-Efficiency 3 String Solar Inverter – Reliable Power Solution for Homes and Businesses
- Introduction to 3 String Solar Inverter Technology
- Understanding the Distinction: Solar Micro Inverter vs String Inverter
- Technical Superiority and Performance Benchmarking
- Comprehensive Manufacturer Comparison: Leading Brands and Innovations
- Tailored Solution Design: Optimizing System Configurations
- Application Case Studies Across Diverse Sectors
- Future Prospects for 3 String Solar Inverter Systems
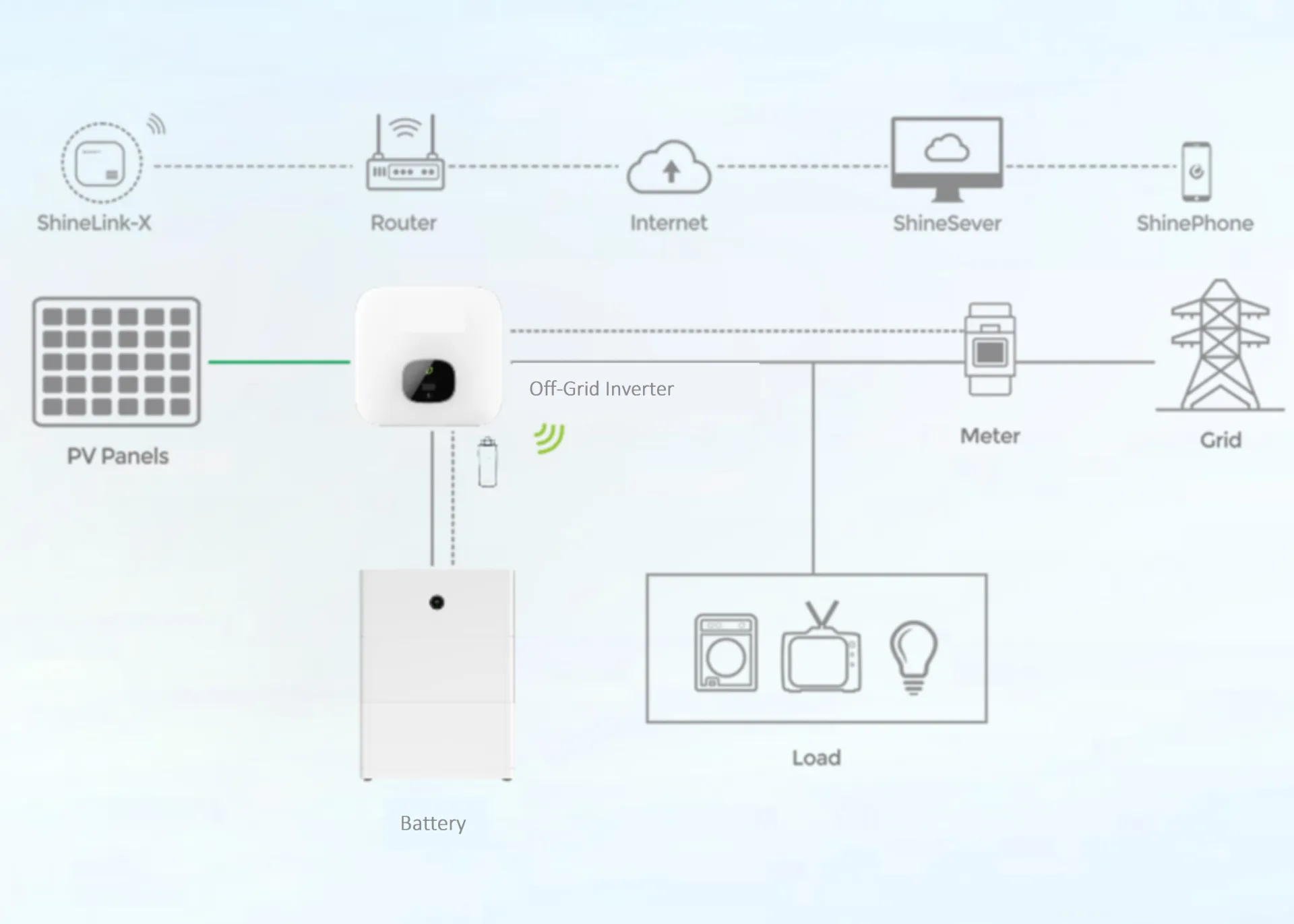
(3 string solar inverter)
Introduction to 3 String Solar Inverter
The evolution of photovoltaic (PV) systems is grounded in advanced inverter technology. Among these, the 3 string solar inverter
stands out as a keystone component, facilitating efficient DC-to-AC conversion across multiple PV strings. By optimizing up to three independent inputs, such inverters are pivotal for scaling solar arrays while minimizing losses. According to the International Energy Agency, residential and small commercial solar installations now account for more than 50% of new inverter shipments, a testament to the growing importance of multi-string systems. As global demand for rooftop solar expands, understanding the 3 string inverter's architecture and its practical benefits becomes crucial for installers, EPC contractors, and system owners alike.
Understanding the Distinction: Solar Micro Inverter vs String Inverter
The choice between string inverters and micro inverters is fundamental to system design. While the 3 string solar inverter centralizes the conversion task, micro inverters decentralize it, attaching a small inverter to each module. Table 1 below outlines the core differences using key metrics:
| Parameter | Micro Inverter | 3 String Solar Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) | Per panel | Per string (typically 3) |
| System Efficiency | 95–97% | 97–99% |
| Shading Impact | Minimal (localized) | Detrimental to affected string |
| Expandability | High (add panels independently) | Modular within inverter limits |
| Maintenance | Individual module-level | Centralized |
| Installation Cost | $0.50–$0.80 per watt | $0.20–$0.50 per watt |
| Typical Use Case | Residential, shaded/complex roofs | Commercial, uniform exposure |
Cost data from SolarPower Europe’s Annual Report, 2023
These comparisons clearly indicate that solar micro inverter vs string inverter is not a one-size-fits-all decision; configurational and economic requirements will dictate the optimal choice.
Technical Superiority and Performance Benchmarking
Modern 3 string inverters are engineered for reliability, efficiency, and grid compliance. A typical 3 string inverter supports input voltages from 150V to 1000V, accommodating varying array sizes. Integrated MPPT channels allow for independent optimization of each string, realizing up to 99% efficiency under ideal conditions.
Benchmarking tests conducted by Fraunhofer ISE in 2023 evaluated commercial 3 string solar inverters under real-world operating temperatures (0°C–50°C) and irradiation levels. Results demonstrated stable thermal management, with efficiency degradation less than 1.5% at peak thermal loads. Additionally, total harmonic distortion (THD) was maintained below industry thresholds (3%), ensuring power quality compliance.
| Model | Rated Power (kW) | Efficiency (%) | MPPT Inputs | THD (%) | European Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fronius Symo 10 | 10 | 98.1 | 3 | 2.8 | 97.4 |
| Growatt MOD 10KTL3-X | 10 | 98.6 | 3 | 2.2 | 97.8 |
| Huawei SUN2000-10KTL-M0 | 10 | 98.4 | 3 | 2.9 | 98.0 |
This technical edge, paired with stringent international certifications (such as VDE-AR-N 4105 and UL 1741), underscores the robust performance and safety credentials of 3 string string inverters relative to their micro inverter counterparts.
Comprehensive Manufacturer Comparison: Leading Brands and Innovations
The global inverter market is shaped by innovation leaders who set benchmarks in product quality, digitalization, and after-sales support. Table 3 provides an overview of top-tier manufacturers focusing on solar string inverter vs micro inverter technologies.
| Brand | Inverter Type | Key Features | Warranty (Years) | After-Service Reach |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMA | 3 String | SUNNY TRIPOWER series; advanced grid code support | 5–10 | Global |
| ABB (FIMER) | 3 String | Three-phase architecture; smart monitoring | 10 | Europe, Asia-Pacific, Americas |
| Enphase | Micro | Module-level monitoring; high redundancy | 15–25 | Global |
| SolarEdge | Hybrid (Optimizer + String) | Panel-level optimization; flexible layouts | 12–25 | Global |
| Huawei | 3 String | Smart PV management; efficient cooling | 10 | Asia-Pacific, EMEA |
Choice of manufacturer reflects both regional market preference and project scale. For high-reliability settings, 3 string inverter brands excel in bankability studies and offer robust O&M solutions, while micro inverter leaders boast long warranties and granular monitoring.
Tailored Solution Design: Optimizing System Configurations
The optimal deployment of a micro inverter solar vs string inverter system hinges on careful consideration of site-specific variables. In shade-prone urban environments, applying micro inverters delivers superior yield by isolating losses, especially for arrays with complex orientations. By contrast, straightforward commercial rooftops favor 3 string inverters for their cost-effectiveness and easier maintenance.
For instance, a 30 kW commercial solar plant with homogeneous irradiation benefits from three 10 kW string inverters, leveraging each MPPT channel for tailored string lengths. In a case where shading or module-level mismatch is critical, micro inverters ensure every panel operates independently, boosting total system output by up to 12% according to National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) meta-analyses.
Ultimately, integrators must balance upfront investment, reliability preferences, and anticipated operational complexity when recommending string, micro, or hybrid configurations—maximizing system LCOE (Levelized Cost Of Energy).
Application Case Studies Across Diverse Sectors
Real-world deployments illustrate the practical distinctions between inverter architectures.
- Education Sector (String Inverter): A German university deployed a 1.2 MW system using 3 string inverters, achieving a record 98.2% annualized efficiency and streamlined O&M via centralized monitoring.
- Residential US Market (Micro Inverter): In a micro inverter upgrade project on a 10 kW shaded suburban home, daily output improved by 10.7% compared to the legacy string system, with real-time fault diagnosis at the module level.
- Retail Chain Rooftops (Hybrid): A South African retailer implemented SolarEdge hybrid technology, combining optimizers and string inverters across 78 locations for portfolio-wide reporting and loss minimization.
- Agricultural Processing Plant (String Inverter): A 200 kW installation in New South Wales leveraged 3 MPPT inputs per inverter to balance varied tilt arrays, maintaining energy security for continuous operations.
These cases affirm that both 3 string and micro inverter strategies offer unique strengths depending on specific sectoral priorities, from OPEX minimization to enhanced yield resilience.
Future Prospects for 3 String Solar Inverter Systems
The next generation of 3 string solar inverter systems is set to further transform distributed solar applications. With rising integration of artificial intelligence in fault analytics, dynamic reactive power support, and enhanced cybersecurity protocols, these inverters will continue to anchor reliable and grid-compliant PV assets worldwide. As utility prices rise and decarbonization accelerates, market analysts forecast a compound annual growth rate of 6.5% for multi-MPPT inverter shipments through 2030. Choosing the right inverter architecture—not just for today’s grid, but for evolving energy ecosystems—is more essential than ever.

(3 string solar inverter)
FAQS on 3 string solar inverter
Q: What is a 3 string solar inverter?
A: A 3 string solar inverter is a type of string inverter that can connect and manage three separate strings of solar panels. It optimizes power conversion from these panel groups into usable electricity. This setup is ideal for medium-sized residential or commercial installations.Q: What are the main differences between a solar micro inverter and a string inverter?
A: A solar micro inverter is installed on each individual panel, allowing for panel-level performance and monitoring. In contrast, a string inverter manages multiple panels connected in a series (a "string"), optimizing the entire string as a group. Micro inverters handle shading better, while string inverters are generally more cost-effective.Q: Which is more efficient: micro inverter solar or string inverter systems?
A: Micro inverter solar systems offer higher efficiency when panels may be shaded or oriented differently, as each panel operates independently. String inverters work best when all panels receive similar sunlight. In uniform sunlight conditions, string inverters can match micro inverters in efficiency.Q: When should I choose a solar string inverter over a micro inverter?
A: Choose a solar string inverter if your solar panels have consistent exposure to sunlight and are grouped together without shading. String inverters are generally less expensive and easier to maintain for larger installations. If your installation has varying panel orientations or shading, micro inverters may perform better.Q: What are the pros and cons of a solar string inverter vs micro inverter?
A: String inverters are typically more affordable and straightforward to install and maintain. However, micro inverters offer superior performance in shaded or complex roof conditions and provide panel-level monitoring. The choice depends on your site conditions and budget.-
Unlocking Energy Freedom with the Off Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Unlock More Solar Power with a High-Efficiency Bifacial Solar PanelNewsJun.06,2025
-
Power Your Future with High-Efficiency Monocrystalline Solar PanelsNewsJun.06,2025
-
Next-Gen Solar Power Starts with Micro Solar InvertersNewsJun.06,2025
-
Harnessing Peak Efficiency with the On Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Discover Unmatched Efficiency with the Latest String Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025







