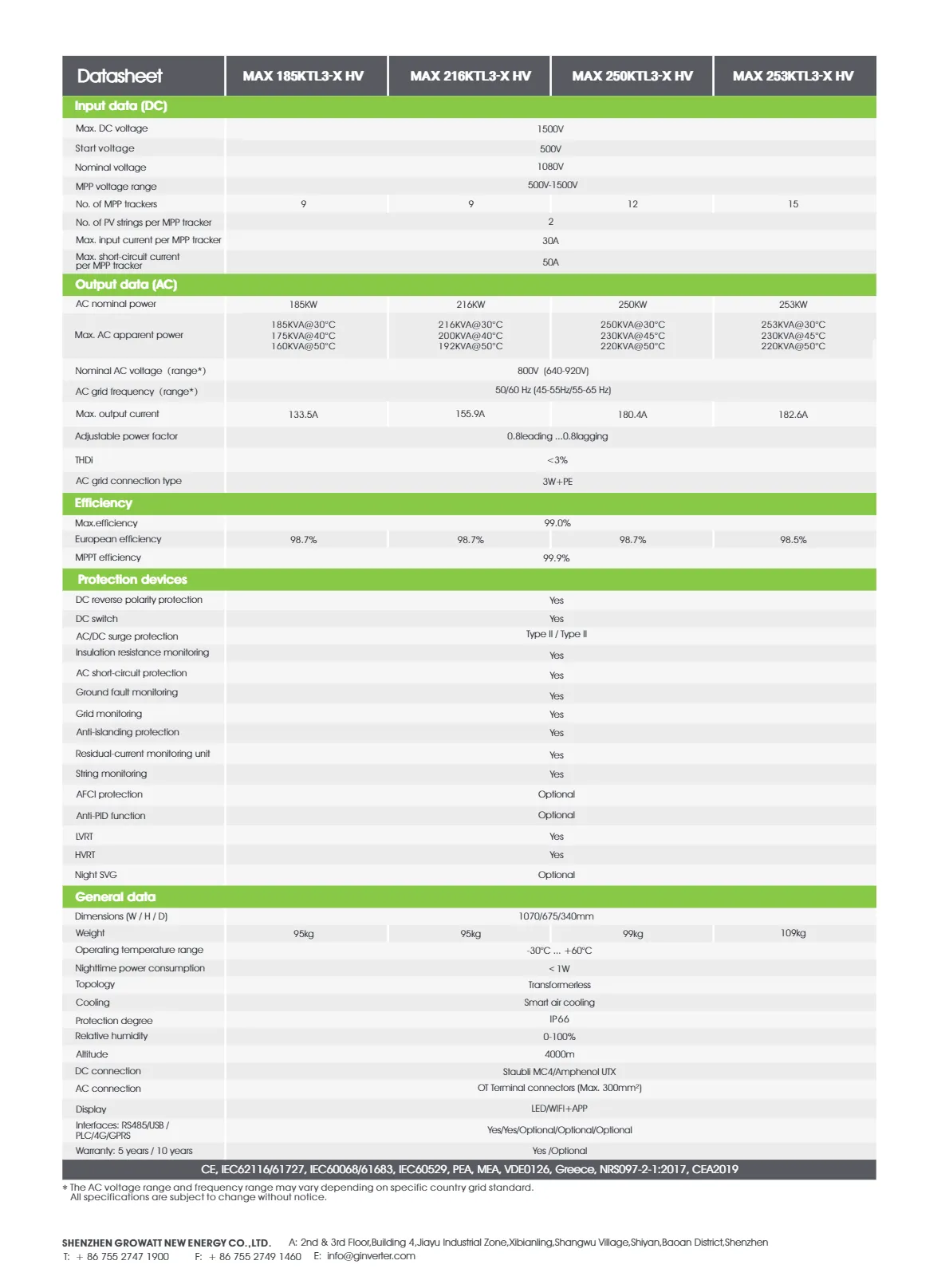
types of solar panels
Types of Solar Panels A Comprehensive Overview
Solar panels have become an essential component of renewable energy systems, capturing sunlight and converting it into usable electricity. As the demand for sustainable energy solutions grows, various types of solar panels have emerged, each with its own unique features, advantages, and considerations. Understanding these types can help consumers make informed decisions about their solar energy needs.
1. Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels are made from a single crystal structure, usually silicon. They are recognized for their high efficiency, often exceeding 20%. The uniform dark color and rounded edges of these panels are distinctive features. One of the greatest advantages of monocrystalline panels is their space efficiency; they produce more power per square meter compared to other types. However, they can be more expensive due to the intricate manufacturing process.
2. Polycrystalline Solar Panels
In contrast, polycrystalline solar panels are composed of multiple silicon crystals melted together. These panels are identifiable by their bluish hue and speckled appearance. While they tend to be slightly less efficient than monocrystalline panels, with efficiencies ranging from 15% to 20%, they are generally more affordable. The production process for polycrystalline panels is usually simpler and requires less energy, making them an attractive option for cost-conscious consumers. However, they take up more space to produce the same amount of electricity.
3. Thin-Film Solar Panels
types of solar panels
Thin-film solar panels are made by depositing one or more thin layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate. This type includes various materials, such as cadmium telluride (CdTe) and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS). Thin-film panels are lightweight, flexible, and can be produced in large quantities, making them suitable for a range of applications, including building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV). However, their efficiency is typically lower than crystalline panels, generally ranging from 10% to 12%. This may necessitate larger installations to achieve desired energy output.
4. Bifacial Solar Panels
Bifacial solar panels are an innovative design that can capture sunlight on both sides of the panel. This feature allows them to generate more energy, especially in areas with reflective surfaces like white roofing or sand. They are typically available in both monocrystalline and polycrystalline versions and can increase energy output by up to 30%. However, the installation costs may be higher due to the need for specific mounting systems to maximize their effectiveness.
5. Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
BIPV systems integrate solar panels into building materials, such as roofs and windows, allowing for a seamless look while generating electricity. They can be attractive for those who want to utilize solar energy without compromising architectural aesthetics. However, the cost of BIPV systems can be significantly higher than traditional solar panel systems, and their efficiency varies greatly depending on the material used.
Conclusion
Choosing the right type of solar panel depends on individual needs, budget, and specific circumstances such as available space and local climate. Each type—monocrystalline, polycrystalline, thin-film, bifacial, and BIPV—offers unique strengths and weaknesses. By understanding these options, consumers can make smarter choices towards harnessing solar energy and contributing to a more sustainable future.
-
Unlocking Energy Freedom with the Off Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Unlock More Solar Power with a High-Efficiency Bifacial Solar PanelNewsJun.06,2025
-
Power Your Future with High-Efficiency Monocrystalline Solar PanelsNewsJun.06,2025
-
Next-Gen Solar Power Starts with Micro Solar InvertersNewsJun.06,2025
-
Harnessing Peak Efficiency with the On Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Discover Unmatched Efficiency with the Latest String Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025







