types of solar panels
Types of Solar Panels A Comprehensive Overview
Solar panels have become a prominent renewable energy source worldwide, transforming sunlight into usable electric power. They are designed to harness solar energy effectively, and their design and functionality vary based on different technologies. Understanding the various types of solar panels available can help homeowners and businesses make informed decisions about their solar energy systems. In this article, we will explore the three primary types of solar panels monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film, as well as their advantages, disadvantages, and typical applications.
1. Monocrystalline Solar Panels
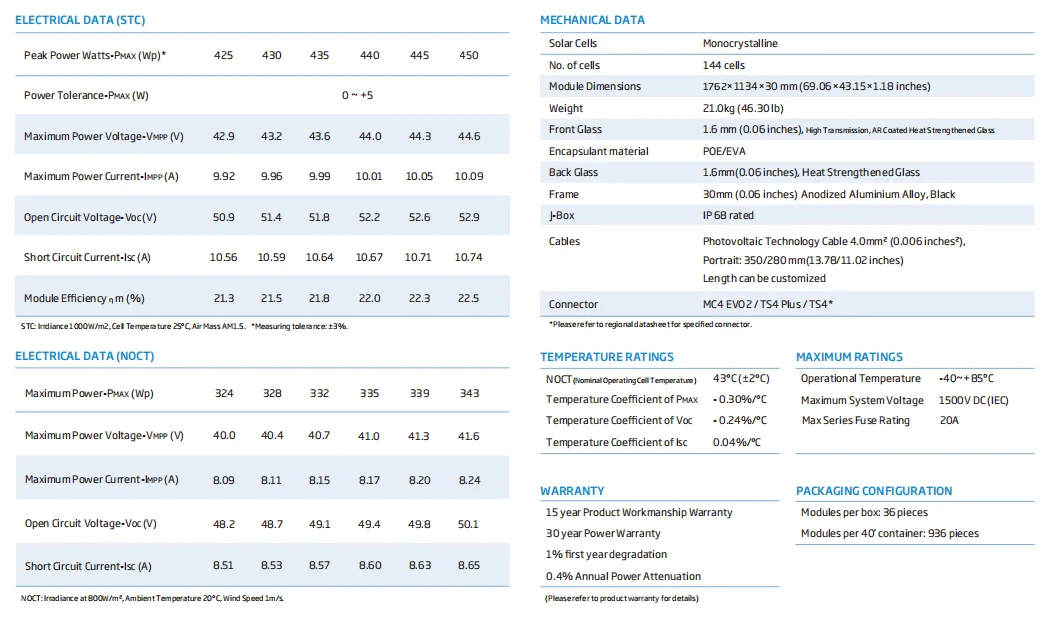
Monocrystalline solar panels are made from a single crystalline structure of silicon. These panels are easily recognized by their uniform dark color and rounded edges. They are known for their high efficiency—typically ranging from 15% to over 22%. This means that they can convert a significant amount of sunlight into electricity compared to other types of solar panels, making them an excellent choice for areas with limited space.
Advantages - Higher efficiency rates. - Space-efficient design, requiring fewer panels for the same energy output. - Long lifespan, often backed by 25-year warranties. - Performs well in low-light conditions.
Disadvantages - Higher cost due to the more intricate manufacturing process. - More sensitive to high temperatures, which may reduce efficiency in extremely hot climates.
Monocrystalline panels are ideal for residential rooftop installations where space may be limited but high energy output is desired. They are often favored in urban settings where homeowners want to maximize their energy generation without needing extensive roof space.
2. Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Polycrystalline solar panels are made from multiple silicon crystals melted together to form a single, solid piece. This manufacturing process gives these panels a distinctive bluish hue with a less uniform appearance compared to monocrystalline panels. While they are slightly less efficient—typically ranging from 13% to 16%—they are also more cost-effective and easier to produce.
Advantages - Lower manufacturing costs lead to reduced pricing for consumers. - Better performance in high temperatures compared to monocrystalline panels. - Generally, a viable option for large-scale solar installations due to their affordability.
types of solar panels
Disadvantages - Lower overall efficiency means that more space is needed to produce the same energy output as monocrystalline panels. - Takes up more roof space, which might be challenging for smaller rooftops.
Polycrystalline panels are well-suited for larger properties or solar farms where space is less of a constraint, and cost-effectiveness is a primary consideration. Many commercial installations choose polycrystalline panels for this reason.
3. Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels encompass a variety of materials, including amorphous silicon, cadmium telluride (CdTe), and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS). These panels are incredibly lightweight and flexible, making them versatile for various applications beyond traditional rooftop installations, such as building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV).
Advantages - Lightweight and flexible, which allows for innovative installation options. - Lower cost and quicker manufacturing process compared to crystalline panels. - Better performance in partial shading and low-light conditions.
Disadvantages - Lower efficiency rates, typically ranging from 10% to 12%, meaning more panels are required to generate the same amount of electricity. - Shorter lifespan and warranties compared to monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels.
Thin-film panels are particularly advantageous in applications where weight and flexibility are crucial, such as on vehicles, portable solar chargers, or in commercial structures where integration into the design is needed.
Conclusion
Choosing the right type of solar panel depends on a variety of factors, including budget, space availability, and specific energy needs. Monocrystalline panels offer high efficiency and meet the demands of space-limited environments, while polycrystalline panels are perfect for those pursuing cost-effective solutions. Thin-film panels provide flexibility and innovative applications. Understanding these differences can greatly influence the effectiveness of a solar energy investment, ultimately leading to substantial energy savings and a reduced carbon footprint. As technology continues to improve, solar energy remains a promising resource in our transition to sustainable energy solutions.
-
Unlocking Energy Freedom with the Off Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Unlock More Solar Power with a High-Efficiency Bifacial Solar PanelNewsJun.06,2025
-
Power Your Future with High-Efficiency Monocrystalline Solar PanelsNewsJun.06,2025
-
Next-Gen Solar Power Starts with Micro Solar InvertersNewsJun.06,2025
-
Harnessing Peak Efficiency with the On Grid Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025
-
Discover Unmatched Efficiency with the Latest String Solar InverterNewsJun.06,2025







